Drupal is an open source CMS and/or framework that is used by at least 2.2 percent of all websites on the internet, making it the world’s third most popular CMS. It is also utilized by the governments of several nations. A content management system (CMS) such as Drupal makes it simple to go online. The modules make it straight-forward for site administrators to organize, edit, and manage material on Drupal.Despite the advantages, additional security risks arise as they do with any significant platform. Have you ever considered what would happen if an unauthorized individual obtained access to your Drupal website’s backend through an admin or editor login? Your organization risks breaching GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) if user data or other sensitive information kept on your website is exposed, in addition to the risk of your website being defaced or even taken down completely by such an assault.Hence, two-factor authentication (2FA) is a must-have security precaution for any conscientious business or organization that wants to drastically reduce the danger of any of its essential Drupal user accounts being compromised. Adding this simple extra login step for administrators and site editors could mean the difference between your site remaining safe and a critical user account being hacked and exploited by a cyber security assault.Follow our comprehensive tutorial below to learn how to improve your Drupal security, optimize the 2FA and avoid being hacked or being a victim of the next digital brute-force assault.


 The more advanced concerns that will be covered in this article are code creation in the Google Authenticator program and codes sent to an email address.
The more advanced concerns that will be covered in this article are code creation in the Google Authenticator program and codes sent to an email address.
 Access bypass vulnerabilities, which enable users to access material that they should not be able to access, and denial of service flaws, which allow attackers to deactivate Drupal sites, are other prevalent forms of Drupal vulnerabilities.When a Drupal security vulnerability is uncovered, the Drupal community publishes a security advisory. These contain details on the sort of attack to expect and the conditions that allow it to be carried out. Some vulnerabilities affect all Drupal installations, while others affect just specific modules or necessitate specific Drupal setups.
Access bypass vulnerabilities, which enable users to access material that they should not be able to access, and denial of service flaws, which allow attackers to deactivate Drupal sites, are other prevalent forms of Drupal vulnerabilities.When a Drupal security vulnerability is uncovered, the Drupal community publishes a security advisory. These contain details on the sort of attack to expect and the conditions that allow it to be carried out. Some vulnerabilities affect all Drupal installations, while others affect just specific modules or necessitate specific Drupal setups.











Table of contents
show
1. What Is Drupal?
Drupal is a PHP-based modular framework and CMS. It allows you to generate and organize material, customize its design, automate administrative operations, and provide rights and responsibilities to users and contributors. It works with any operating system. It does, however, require a PHP-compliant HTTP server, such as Apache Server, and a database server, such as MySQL, to function.The Drupal framework is usually referred to as a Content Management Framework because, in addition to offering basic CMS capabilities, it also implements a set of sophisticated application programming interfaces and has a modular structure that allows for the building of comprehensive modules. This feature is so eye-catching that the Drupal developer community is extremely vocal about it.
2. What Is 2FA?
Two-step authentication (2FA) is a technique of verifying a user’s identity when they log in. It consists of two verification processes. The first way is the well-known login, which entails inputting a username and password. The risk of assaults and the chance that someone unauthorized gains access to your account has increased as a result of online development and the creation of many services that store sensitive data, such as Facebook or GitHub. The second way of authentication was created to avoid such a problem. The approach doesn’t guarantee that your data is safe 100 percent of the time, but it significantly enhances data security in Drupal, for example. The following are the most popular ways for second authentication during login:- A code delivered via SMS.
- A list of produced codes to be utilized.
- The production of access codes in third-party programs like Google Authenticator.

3. How Drupal works?
According to the GPL/GNU license, anybody may inspect Drupal’s workings, make adjustments, redistribute with or without modifications, and propose changes to the main project as an open-source project. The Drupal community is vibrant and supportive. Several Drupal community modules with critical functionalities were written by regular users.Drupal, as a dynamic platform, provides a plethora of capabilities, including CMS, blogs, discussion-based software, collaboration tools, and an all in one package that is free to install and simple to use. An administrator may create a one-of-a-kind Drupal-based website that combines knowledge management, online publishing, and community engagement by activating and configuring distinct modules.⇨ How to implement the 2FA in Drupal?Installing and configuring various modules is all that is required to implement the basic version of this feature. The basic version provides the following features:- Modifying the Drupal login procedure.
- Creating a new block with a login form.
- Generating text access codes.
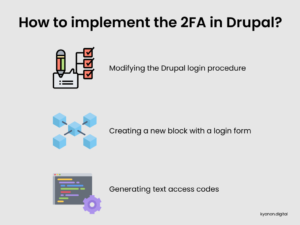 The more advanced concerns that will be covered in this article are code creation in the Google Authenticator program and codes sent to an email address.
The more advanced concerns that will be covered in this article are code creation in the Google Authenticator program and codes sent to an email address.4. What is the significance of Drupal security?
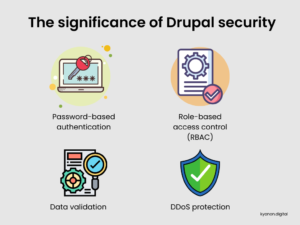
Drupal is built with the goal of being as safe as possible by default. It has a number of security measures that guard against various forms of threats:- Password-based authentication: Drupal accounts are protected by encrypted passwords. Furthermore, Drupal is built to identify and immediately shut down brute-force password assaults, which are efforts by an attacker to guess a password by cycling through multiple possibilities.
- Role-based access control (RBAC): Drupal features an RBAC architecture that allows administrators to grant different levels of access to different accounts. This allows some users to execute things that are disabled for other accounts. For example, you may grant certain accounts read-only access to website material while others have the ability to alter the content.
- Data validation: To sanitize data and avoid injection attacks, the Drupal API conducts various automated tests.
- DDoS protection: Drupal caches material to assist prevent the effect of distributed denial of service (DDoS) assaults, which aim to overload a website with malicious requests in order to shut it down.
5. What are the security flaws and threats of Drupal?
While Drupal is well-established and popular, it, like any CMS, is vulnerable to a wide range of possible security flaws. Attackers can use these flaws to steal private data, take control of Drupal-hosted servers, publish harmful or objectionable material on a Drupal-powered website, and more.However, Drupal has a reputation for being more secure than other popular CMS platforms. It has an active security team of developers who work to find, announce, and address Drupal security concerns. Because Drupal is open source, anybody may examine its source code and check it for vulnerabilities, which helps to prevent security issues.Despite this, security flaws in Drupal do occur, with remote code execution attacks being among the most deadly. This form of vulnerability is when an attacker installs malicious software on the machine that hosts a Drupal installation. In 2018, two serious remote code execution vulnerabilities affecting Drupal 7 and 8, known as drupalgeddon2 and drupalgeddon3, were announced and resolved. Access bypass vulnerabilities, which enable users to access material that they should not be able to access, and denial of service flaws, which allow attackers to deactivate Drupal sites, are other prevalent forms of Drupal vulnerabilities.When a Drupal security vulnerability is uncovered, the Drupal community publishes a security advisory. These contain details on the sort of attack to expect and the conditions that allow it to be carried out. Some vulnerabilities affect all Drupal installations, while others affect just specific modules or necessitate specific Drupal setups.
Access bypass vulnerabilities, which enable users to access material that they should not be able to access, and denial of service flaws, which allow attackers to deactivate Drupal sites, are other prevalent forms of Drupal vulnerabilities.When a Drupal security vulnerability is uncovered, the Drupal community publishes a security advisory. These contain details on the sort of attack to expect and the conditions that allow it to be carried out. Some vulnerabilities affect all Drupal installations, while others affect just specific modules or necessitate specific Drupal setups.6. Recommendations to ensure security in Drupal
Because Drupal is becoming more popular as a CMS, it is constantly at danger of being attacked or hacked. You can never completely prevent these things from happening. But, aside from merely being up to date on Drupal security warnings, there are a few things you can do to make your Drupal installation more safe. To tighten your Drupal security, follow the tips below.
6.1. Assess your site’s security requirements and hazards from the start
The first step in strengthening Drupal security is determining which security issues are the most concerning to you and your users. Ask these crucial questions ahead of time:- Do your Drupal-powered sites hold any particularly sensitive information?
- Are any of your Drupal users or accounts at danger of being compromised?
- Are you vulnerable to specific sorts of assaults because of the industry you work in, the geographical location in which you live, or other factors?

6.2. Drupal Core and modules should be updated
Another simple technique to boost security is to keep your Drupal installation up to date. Modules and themes can be obtained via the Drupal source or from well-known vendors. This will result in less troubles for you in the future. Drupal modules should be updated on a regular basis. You may manually upgrade modules on your Drupal server by replacing each existing module with the most recent version.Make sure that the new modules you install are safe. Using modules that are eligible for security warnings under Drupal’s current policy is an excellent place to start.You should also make sure that your Drupal Core is up to date with the most recent stable release in the version line you’re using. If your hosting provider provides a Drupal installation, you will most likely be able to upgrade to the most recent Drupal version. If not, you may upgrade Drupal Core by manually installing the most recent Drupal package on your server or by using Drush.
6.3. Regularly scan your webpage
While scanning your Drupal-powered website is not a panacea, it can assist in identifying security problems. Drupal sites may be scanned using internet services such as Drupal Security Scan or open source applications such as Droopescan. These, and comparable technologies, will provide reports outlining any security issues they find on your site.
6.4. Customize user permissions
To secure your website, ensure that the necessary file permissions are used. Each directory and file has its own set of rights that enable anyone to read, write, and change it. If your permissions are too lax, an intruder may get access, and if they are too rigorous, your Drupal installation may fail since modules and Drupal core require access to particular folders. The Drupal documentation on safeguarding file rights and ownership is excellent.
6.5. Make use of Drupal security components.
There are several solid Drupal security modules available that will secure your site and help defend it from brute-force attacks. These plugins enable you to block dangerous networks, rate limit or prevent security risks, enforce strong passwords, scan for vulnerabilities, see which files have changed, establish a firewall to prevent common security threats, monitor DNS changes, and much more. Consider utilizing these and additional security modules:- Security Review: This module examines your Drupal setup for weaknesses that might result in security concerns. Because it operates within Drupal rather than merely scanning Drupal sites from the outside, it can uncover issues that normal Drupal scanners might miss.
- Security Kit: This module adds data validation tools to the Drupal API that go beyond what is provided by the Drupal API. Security Kit aids in the prevention of code injection attacks, which are carried out by introducing malicious instructions into Drupal sites.
- Password Policy: This module may be used to assist users in creating safe passwords for their Drupal accounts by mandating them to include numbers and special symbols in their passwords, for example.
- Login Security: Set a limit on the number of login attempts and block access based on IP address.
- Access control list (ACL): Access control lists for node access.
- Captcha: Prevent spam bots and programs from filling out forms.
- Automated Logout: Provides administrators with the ability to log out users after a predefined time period.
- Session Limit: Set a limit on the number of concurrent sessions per user.
- Material Access: Permissions for different sorts of content based on role and author.
- Coder: This person validates your Drupal code against coding standards and best practices.
- SpamSpan filter: Encrypts email addresses to prevent spammers from gathering them.
6.6. Choose a hosting company that focuses on security
Drupal can work on almost any hosting platform, but it’s best to go with a hosting company that prioritizes security. Hosting systems with dedicated virtual servers, rather than shared accounts on the same servers, are more secure. You should also ensure that the operating systems deployed on your hosting provider’s servers are patched and up to date.
6.7. Utilize an SSL certificate
SSL certificates encrypt network communication, making it more difficult for attackers to eavesdrop on data as it passes between servers and client devices. An attacker might possibly “sniff” data as it travels across the network and read it in order to obtain sensitive information stored on your Drupal site if SSL encryption is not used. An SSL certificate also acts as confirmation that your website is legitimate, allowing visitors to trust it and avoid fake imitations.
6.8 Take caution when handling confidential information
Take adequate measures if your Drupal site contains data that is highly sensitive or subject to regulatory safeguards, such as healthcare information or payment-processing data. Make that the data is encrypted both at rest and in transit, and limit access to the data to the user accounts who need it.Consider whether there is any purpose to incorporate sensitive data on your Drupal site. If not, simply do not host it there in the first place. Drupal is not meant to be a general-purpose data storage system. Instead, it should only be used to create and manage material that must be made available over the Internet.
6.9. Make regular backups
Backing up your Drupal site and data will not make it less likely to be attacked, but it will help you survive a data breach. If you keep frequent backups, you can quickly roll back if you are attacked and restore your CMS. We also recommend that you make backups before updating your Drupal core and modules.Backing up Drupal may be done in a variety of ways. Some Drupal hosting managers, such as Pantheon, provide one-click backup and restore as well as development environments. Or you could take a snapshot of the complete server that runs Drupal, or you could utilize a Drupal module like All In One Backup to backup all of the data within your Drupal setup. Managed backup companies can automate the backup procedure for you if you prefer a hands-off approach.
6.10. Select appropriate passwords and usernames
Strong passwords serve to set the groundwork for Drupal’s, and any software platform’s, security. The key to selecting a decent password is to ensure that it does not exist in a dictionary file, which is a collection of known passwords that an attacker may try while attempting to brute-force a login. Passwords of at least eight characters in length that include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special symbols are unlikely to be discovered in a dictionary file.Changing the default username can also assist to increase password security. If attackers do not know the usernames connected with your accounts, that information becomes a secondary component that they must compromise before they can get access.
7. Conclusion: How to ensure security in Drupal?
As you can see, there are several ways to strengthen your Drupal security. Keeping your Drupal core and modules up to date, using safe usernames and passwords, utilizing security plugins, secure connections, database security tactics, two-factor authentication, file permissions, using an SSL certificate, and more. Many of these suggestions may be applied in a matter of minutes, and allow you to rest certain that your Drupal site is now a little more safe against intruders and hackers.Regardless of how much Drupal knowledge you have, improving security may be difficult. Keeping up with the ever-changing list of security vulnerabilities and compliance standards that affect modern developers and IT teams, is also important. As a result, collaborating with a team of experts that specialize in maintaining and improving Drupal and other business-critical programs, may help you take your security approach to the next level. Request more information about Kyanon Digital‘s extensive Drupal development company to see how we can assist you.
5/5 - (1 vote)



