Software development outsourcing has played a vital role in business strategies, since there are rapid changes in technology and digitization has been a key driver for enterprises’ development. Through this article, Kyanon Digital wishes to explain in depth what software development outsourcing is about, and 50 terms you should know when it comes to Software Development Outsourcing.
1. What is Software Development Outsourcing?
Software Development Outsourcing describes an arrangement, in which an organization decides to hire an external software development agency to efficiently perform every task of a software development project that could be done in-house instead. Software outsourcing is about the practice of a company handing over the control of a certain business process or project to a third-party vendor that is qualified and capable of handling the required business tasks.

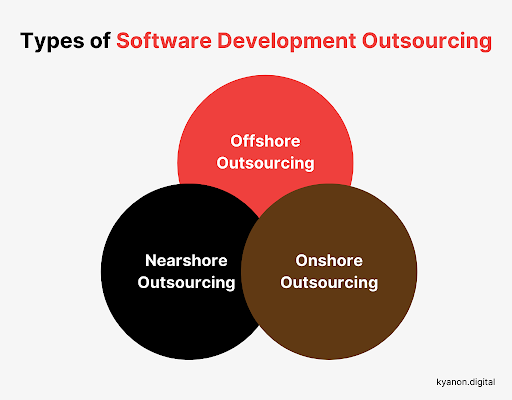
2. Types of Software Development Outsourcing services
2.1. Offshore Outsourcing:
Working with a reliable software outsourcing company from distant countries. Here, cost-effectiveness will be the first mention for offshore outsourcing because of its low labor costs. Besides that, multiple resources are another advantage of offshoring. However, language and cultural differences might bring issues to both parties. Regular meeting and researching culture before developing the product would help in some way.
2.2. Nearshore Outsourcing:
Delegating software development responsibilities to an extended team in a nearby country, usually in similar time zones. It can help outsourcing become more effective. Because of the closing in geography and time, there will be no gap in time zone, culture, and communication. Besides that, it can be easy for clients to visit and meet the outsourcing development team in person. This convenience can help to figure out the crucial issues relating to the software outsourcing development process (if any).
2.3. Onshore Outsourcing:
Hiring services to assist your company from within the same country. No language barriers can be the advantage of this type of outsourcing because both parties speak the same language. It can help outsourcing become more effective. Yet, clients may have to pay for development costs higher than nearshoring and offshoring.
3. Relationship-based Outsourcing
Relationship-based outsourcing is classified based on business objectives and the type of management your project requires. According to these criteria, the two most common outsourcing models are:
3.1. The project-based:
When a client company requires additional technical expertise for a project, they hire an outsourcing development team to build the product and manage the workflow. The scope of work (as well as the payments) is fixed and intended for quick completion and delivery.
3.2. The specialist model:
The specialist model entails the hired outsourcing company developing the product (filling gaps in the company’s technical knowledge) under the control of the client project manager or an in-house team. The adaptable work scope distinguishes this model (and the flexible rates, paid hourly or monthly). It is done to supplement the client’s company’s staff.
4. 50 Software Development Outsourcing terms to know
- A
– Agile (n): A software development approach that implies iterative software development, flexible planning, and continuous improvement.
– Acceptance Testing (n): A test conducted to determine if the requirements of a specification or contract are met.
– API (Application Programming Interface) (n): A set of defined rules that enable different applications to communicate with each other.
– AWS (Amazon Web Services) (n): A cloud computing platform provided by Amazon.
– Azure (n): Microsoft’s cloud computing platform.
- B
– Backend (n): Backend development essentially refers to everything that goes on behind the scenes without users’ direct interaction. It is a data access layer, the way the software works.
– BOT Model (Build-Operate-Transfer Model) (n): An engagement model where the outsourcing provider builds and operates the software project for a period of time, and then transfers ownership and control of the project to the client.
- C
– CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery or Deployment) (n): A set of rules, principles and procedures used to deliver applications to end-users by including more automation in the development process.
– Confidentiality of Software (n): Licensee acknowledges that the Application Software is confidential in nature and constitutes a trade secret belonging to Licensor.
- D
– Data Confidentiality (n): Personal data, trade secrets, and other private business data are protected against unauthorized access, disclosure without permission, and theft.
– DevOps (Development Operations) (n): System of working that helps to keep development, IT operations, and quality assurance departments on the same page to make for better end-products and collaborations.
– Dedicated Team (n): A business model that refers to an agreement between the client and service provider, when the latter provides software development professionals to the client on a long term basis.
– DPA (Data Processing Agreement) (n): An agreement between the data controller and the data processor, with intention to regulate data processing by the parties as well as the relationship between the parties .
– Docker (n): A containerization platform that allows developers to package applications into containers that can run on any platform.
- F
– Frontend (n): A ‘client’ software that the users interact with. It is a presentation layer, the way the software looks.
– Fixed-Price Contract (n): A flat rate contract where the provider is responsible for completing the project.
– Full-Stack Development (n): A development approach that involves working on both the front-end (client-side) and back-end (server-side) of a software application.
- G
– GCP: Google Cloud Platform, Google’s cloud computing platform.
- I
– IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) (n): A cloud computing model that provides virtualized computing resources over the internet.
- K
– Kubernetes (n): An open-source container orchestration platform used to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
- M
– MSA (Master Service Agreement) (n): An agreement is signed if a company is going to work with a client repeatedly.
– MVP (Minimum Viable Product) (n): A software product with enough features to satisfy early users and collect feedback for future development.
– MVC (Model-View-Controller) (n): A software design pattern that separates an application into three interconnected components: the model, the view, and the controller.
– Microservices (n): A software architecture pattern that structures an application as a collection of small, independent services that can be deployed and scaled independently.
- N
– Non-Solicitation Clause (n): A provision in a contract generally prohibiting the hiring (or attempting to hire) of one of the other party’s employees or contractors.
– NDA (Non-Disclosure Agreement) (n): An agreement is signed to protect sensitive information from being disclosed.
- O
– ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) (n): A technique used to map objects in a software application to relational database tables.
- P
– Project-Based Model (n): Also known as the Outsourced Development Team Model or the Software Outsourcing Model. In this strategy, business owners will contract with a software outsourcing firm and give the end-to-end development team complete control over adhering to the client’s specifications and expectations.
– PaaS (Platform as a Service) (n): A cloud computing model that provides a platform for developing, testing, and deploying software applications.
- Q
– QA (Quality Assurance) (n): A process of product review to identify if it meets required expectations or has any errors.
– QC (Quality Control) (n): A process through which a business seeks to ensure that product quality is maintained or improved.
- R
– RFI (Request for Information) (n): A preliminary document used by companies that do not have enough information about the marketplace they prepare to enter.
– RFP (Request for Proposal) (n): A document that asks vendors to propose solutions to a customer’s problems or business requirements.
– RFQ (Request for Quotation) (n): A specific detailed document that drills down to the exact specifications required by the company.
– RESTful API (Representational State Transfer API) (n): A type of API that uses HTTP requests to retrieve or modify data.
– Risk-Sharing Engagement Model (n): An engagement model where the outsourcing provider shares some of the project risks with the client, and is incentivized to deliver the project within the agreed upon parameters.
- S
– SAAS (Software As A Service) (n): The most basic of cloud platforms; allows users to share files and collaborate on projects through their browser.
– SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle) (n): The process used in software development to build, design, and test high-quality software. It implies three rules: create high-quality software on time, stay within budget, and meet customers expectations.
– SCRUM (n): A project management methodology for effective team collaboration based on the Agile software development approach.
– Staff Augmentation (n): Also known as extended software development, is an outsourcing strategy where businesses rely on a form of outsourcing to meet their technical needs.
– SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) (n): A standard security protocol for ensuring that all data transmitted between the web server and the browser remains encrypted, which is unreadable to the naked eye.
– Software Warranty (n): A form of contract listing the condition and performance of a software that is guaranteed by the software manufacturer.
– Statement of Work (n): A document where both parties describe the crucial details connected with the project.
– SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) (n): A protocol used for exchanging structured information in the implementation of web services
– SLA (Service Level Agreement) (n): A contract between the client and the outsourcing provider that defines the level of service the provider will deliver.
– SDK (Software Development Kit) (n): A collection of software development tools used to create applications for a specific platform or operating system.
– Software IP (Software Intellectual Property) (n): A computer code, software or program that is protected by law against copying, theft, or other use that is not permitted by the owner.
- T
– TT&M Model (Time and Materials Model) (n): A contract that requires payment based on the amount of hours and resources spent on specific projects.
- W
– Waterfall (n): A traditional software development methodology that follows a linear, sequential process.

Kyanon Digital hopes this article has helped you to gain useful information related to Software Outsourcing services. Therefore, you will have a more specific knowledge of this matter to make the best choices for your business. And if you have any questions related to this matter, do not hesitate to contact us for specific consultation.



