The landscape of business is undergoing a significant transformation fueled by the relentless march of artificial intelligence (AI). AI adoption in business is no longer a futuristic vision; it’s a present reality with the potential to revolutionize every aspect of operations, from marketing and customer service to product development and logistics.
In this blog, David Lapetina, VP – Engineering & Technology, Kyanon Digital will walk you through the exciting world of AI adoption in business, exploring both the challenges and opportunities it presents. It uncovers the hurdles businesses face in integrating AI into their workflows and equip you with valuable insights to navigate this transformative journey.
1. AI capabilities for business
The power of AI is revolutionizing the way businesses operate. Kyanon Digital, a full digital services house, especially in AI solutions, stands at the forefront of this transformation, helping businesses leverage AI to unlock new levels of efficiency, productivity, and customer satisfaction.
There are three key areas where Kyanon Digital’s expertise in AI can significantly benefit your business: Smart Retail, Safety in Construction sites and Analytics.
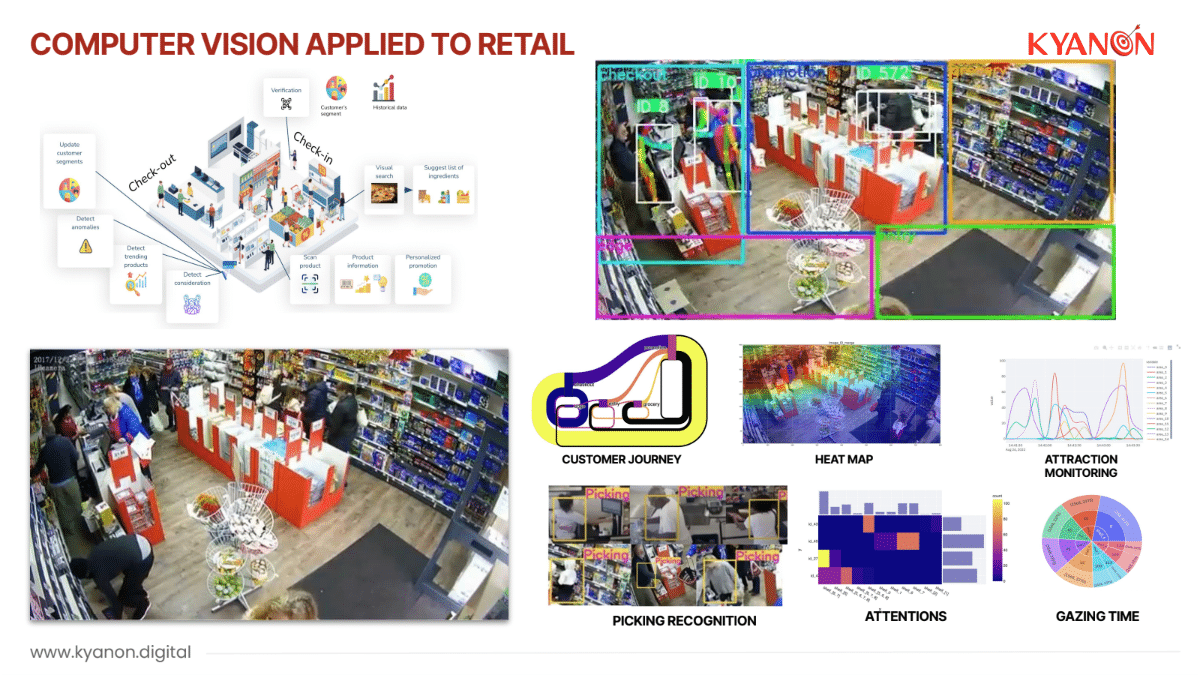
1.1. Smart Retail
Smart retail refers to integrating advanced technologies and data-driven solutions in a traditional retail store. It aims to enhance the overall shopping experience for customers, optimize operations, and improve business outcomes.
Smart retail solutions empower retailers to adapt to changing consumer expectations, create seamless shopping experiences, and stay competitive in today’s dynamic retail landscape.
- Personalized Interactions: Smart retail enables retailers to provide personalized experiences for their customers. Beyond basic e-commerce, brands can offer custom orders or product recommendations based on users’ past purchases and browsing history. Real-time push notifications about new products can be sent to smart devices while customers are still in the store, creating a customized shopping experience even without an online presence.
- Efficient Supply Chain Management: Smart retail tools help reduce waste due to overstock and theft. They increase revenue per square foot by improving inventory accuracy and optimizing stock levels. By tracking inventory location, safety is enhanced, and fewer items remain unused in stock.
- Waste Reduction: Implementing smart retail solutions minimizes waste by streamlining processes, reducing excess inventory, and enhancing inventory management. This leads to cost savings and a more sustainable approach to retail.
- Optimizing Staff Time: Smart retail technologies automate routine tasks, allowing staff to focus on more value-added activities. For instance, automated checkout systems and inventory management tools free up time for personalized customer interactions.
1.2. Safety in Construction sites
AI is a powerful ally in creating safer construction sites, improving worker well-being, and preventing accidents. Its adoption can lead to a more productive and secure construction industry.
Types of AI in Construction Safety:
- Computer Vision: AI-powered cameras enhance on-site visibility and detect non-conformance. They can identify safety violations, unauthorized personnel, and potential hazards.
- Reducing Human Error: Approximately 90% of construction accidents are attributed to human error. AI helps minimize these errors by automating processes and providing real-time alerts.
- Predictive Analysis: AI algorithms analyze historical data to predict potential accidents. By identifying patterns, construction companies can take preventive measures to avoid repeat incidents.
- Wearable Devices: Incorporating AI into wearables (such as smart helmets or vests) allows real-time monitoring of workers’ vital signs, fatigue levels, and exposure to hazardous conditions.
- AI-assisted BIM (Building Information Modeling): Mapping out hazardous areas and visualizing safety risks using BIM models improves decision-making and planning.

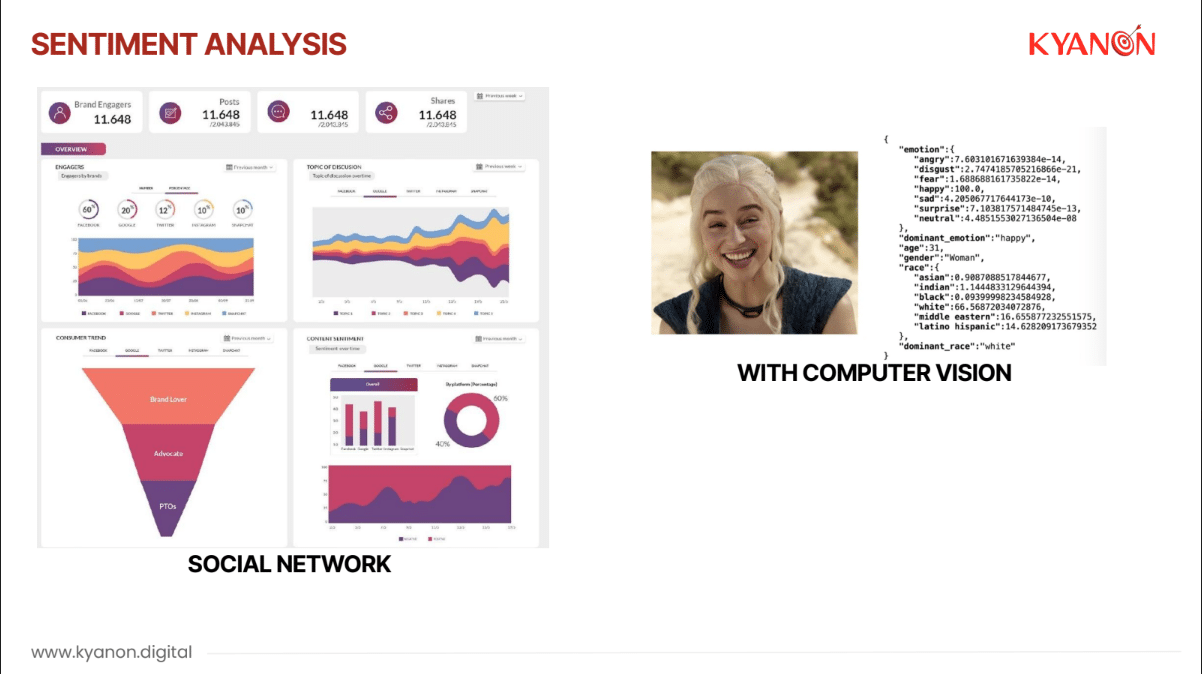
1.3. Analytics
AI analytics is a powerful field that combines artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) techniques with traditional data analysis processes. It supercharges data analysis by automating tasks, uncovering hidden patterns, and making data-driven predictions.
At Kyanon Digital, we offer Data and Analytics services, including:
- Data Governance: Empower data intelligence with robust practices and industry-efficient processes, to create craft data-driven and data-centric strategies.
- Data Engineering: A holistic approach to data engineering, and enterprise test data management, that covers all the technical drivers required to fully capitalize on your enterprise data resources.
- BI & Visualization: Present data in intelligent and practical visuals to help you make informed and trailblazing decisions for your business.
- Customer Analytics: Recognize your customers’ journeys and lifetime values, and deploy advanced analytics solutions to fine tune offers and refine marketing initiatives.
- Competitive Intelligence Analytics: Leave your competitors far behind using applicable insights about the industry, and fine tune your marketing and consumer service efforts.
2. Challenges of AI adoption in business
While the potential benefits of AI are undeniable, businesses face several hurdles when integrating it into their operations. Here’s a closer look at some of the key challenges.
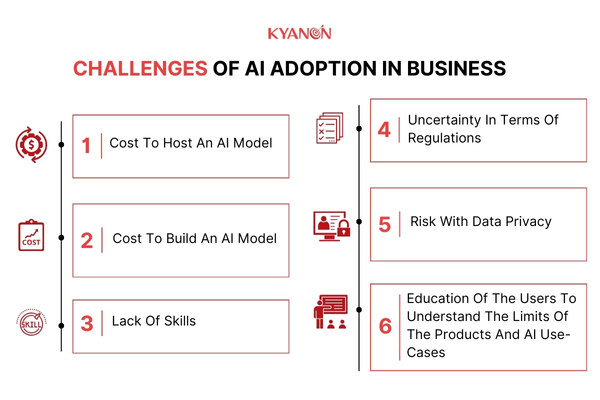
2.1. Cost to host an AI model
AI models, especially deep learning models, require significant processing power to train and run. This translates to hefty cloud hosting fees. Factors influencing cost include:
- High Initial Costs: Implementing AI solutions often requires significant upfront investment. This includes costs related to infrastructure, hardware, software licenses, and skilled personnel.
- Cloud Service Expenses: Many businesses choose to host their AI models on cloud platforms. While this provides scalability and flexibility, it also involves ongoing expenses based on usage and resource allocation.
- Maintenance and Upkeep: Regular maintenance, updates, and monitoring of AI models contribute to operational costs. Ensuring optimal performance and security requires continuous effort.
- Data Storage and Processing: Storing large datasets and processing them for training and inference can be expensive, especially when dealing with high-dimensional data or real-time applications.

2.2. Cost to build an AI model
The cost of building an artificial intelligence (AI) model can vary significantly based on several factors. Let’s explore these key considerations.
- Development Costs: The development costs for an AI model primarily involve designing and building the system. The complexity of the AI application, the chosen technology stack, and the development time all contribute to the overall cost.
- Data-Related Costs: Data is crucial for AI models. Acquiring, cleaning, and managing data can be expensive.
- Infrastructure Costs: Setting up and maintaining the necessary infrastructure is another significant expense. Infrastructure costs include: Hardware, Software, Server Hosting
- Ongoing Maintenance: Regular maintenance, updates, and monitoring contribute to long-term costs. Ensuring optimal performance and security requires continuous effort.

2.3. Lack of skills
One of the significant challenges in adopting artificial intelligence (AI) in business is the lack of skills. Regardless of the industry, understanding the complexities of AI is crucial. Besides that, employees may fear losing their jobs due to AI adoption. Organizers should foster a culture of collaboration and communication, emphasize that AI augments human capabilities and provides assistance, as well as highlight the benefits of AI to improve adoption and create support
Remember, addressing the skills gap is vital for successful AI integration. Organizations must invest in training, foster a supportive culture, and recognize the unique strengths of both humans and AI.

2.4. Uncertainty in terms of regulations
Navigating the regulatory landscape for artificial intelligence (AI) adoption in business presents several challenges, especially when dealing with uncertainty. Let’s explore these challenges.
- Complexity of Regulations: AI technologies often operate in a complex legal and regulatory landscape. Navigating these complexities can be daunting for businesses, especially when deploying AI across multiple regions.
- Rapidly Evolving Regulations: The regulatory environment surrounding AI is continuously evolving as policymakers grapple with the ethical, societal, and economic implications of AI deployment.
- Uncertainty in Interpretation: Even when regulations are in place, there can be uncertainty about how they apply to specific AI applications. Ambiguity in regulatory language and differences in interpretation can lead to confusion and differing compliance approaches among businesses.
- International Differences: Businesses operating globally must contend with not only the regulations of their home country but also those of the countries in which they operate. Bridging the gap between different regulatory frameworks and ensuring compliance across borders adds another layer of complexity.
- Risk Aversion: The uncertainty surrounding regulations can make businesses more risk-averse when it comes to adopting AI technologies. Faced with potential legal and reputational risks, some companies may opt to delay or scale back their AI initiatives until regulatory ambiguities are resolved.

2.5. Risk with Data privacy
Businesses are flocking to AI for its potential to revolutionize everything from marketing to manufacturing. But this rush to embrace AI comes with a big risk: data privacy. Here’s a breakdown of how AI adoption can put data privacy at risk:
- Exposure of sensitive information: AI systems often gobble up massive amounts of data, including personal information like names, addresses, and even financial details. If not properly secured, this data could be exposed in a breach, leading to identity theft and other harms.
- Opaque AI models: Many AI models are complex and difficult to understand, even for their creators. This “black box” effect makes it hard to explain how the AI arrived at a decision, raising concerns about bias and discrimination.
- Data sharing and third-party access: Businesses often share data with third-party vendors to train and maintain AI models. This raises the risk that data could be misused or fall into the wrong hands.
- Data retention and deletion: Knowing how long to store data and when to securely delete it is crucial. Businesses need to have clear policies in place to avoid running afoul of data privacy regulations.
- Inference of sensitive information: Even if you don’t directly feed sensitive data into an AI, it might be able to infer it from other information. For example, an AI analyzing purchasing habits might be able to guess someone’s income or health conditions.

2.6. Education of the users to understand the limits of the products and AI use-cases
One of the key challenges in AI adoption for businesses is user education regarding AI limitations. While AI offers immense potential, it’s crucial for users to understand its boundaries to ensure responsible and effective implementation. Here’s how this lack of user education can pose problems:
- Unrealistic expectations: If users believe AI is flawless, they might rely on its outputs blindly, potentially missing errors or biases. This can lead to poor decision-making and erode trust in the technology.
- Misuse of AI tools: Without understanding the limits of AI capabilities, users might attempt tasks the AI wasn’t designed for. This can lead to inaccurate results and missed opportunities.
- Resistance to change: Users apprehensive about AI due to a lack of understanding might resist its adoption, hindering the potential benefits for the business.
3. Powering Up for the AI Revolution
AI adoption presents a complex maze for businesses, filled with both daunting challenges and promising opportunities. While the potential for increased efficiency, innovation, and profitability is undeniable, navigating data privacy risks, overcoming user limitations, and ensuring responsible implementation require careful consideration.
However, by approaching these challenges with a strategic focus on data security, user education, and a commitment to ethical practices, businesses can harness the power of AI to unlock a new era of competitive advantage. The future of AI in business is not predetermined, and the choices we make today will define the path forward.
By embracing both the challenges and opportunities, businesses can foster a future where AI empowers human ingenuity, creating a more productive and prosperous world. Kyanon Digital is a Full Digital Service House, helping to fuel your business growth with data. Kyanon Digital’s mission is to bridge the gap between lab and business, bringing research theory to practical business problems.
Contact us for more consultation from Data and AI experts in the industry!



