In 2025, the e-commerce fulfillment service global market is worth an estimated $140 billion, up 12.9% year-over-year (YoY). Deeper in, around 60% of online retailers now outsource at least part of their fulfillment operations, and 1 in 5 fully rely on third-party logistics (3PL) partners to manage the entire process (Grandview Research).
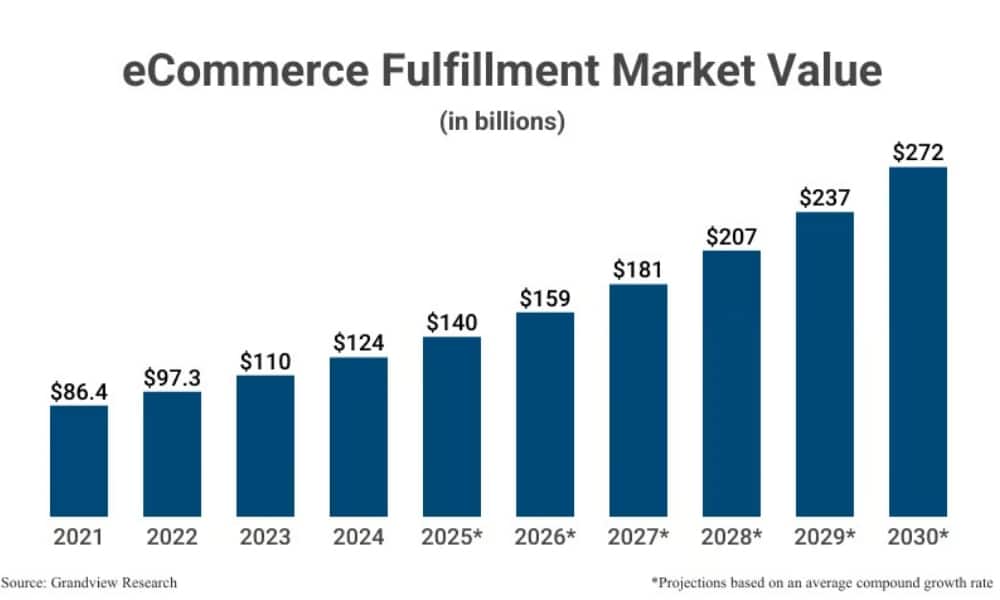
This growing shift reflects the global trend toward tech-enabled, scalable eCommerce fulfillment solutions; more specifically, how fulfillment is evolving from a logistics function into a competitive differentiator, powered by automation, smart inventory placement, and omnichannel integration.
Let’s explore how modern eCommerce fulfillment works, its key processes, and the technology shaping its future, with insights from Kyanon Digital to help enterprises optimize operations and scale sustainably.
Key takeaways
- eCommerce fulfillment is a core business driver: impacting delivery speed, accuracy, and customer satisfaction.
- Modern fulfillment leverages technology: AI forecasting, warehouse automation, digital twins, and omnichannel integration boost efficiency and scalability.
- Choosing the right fulfillment model: in-house, 3PL, dropshipping, or hybrid-affects cost, control, and brand experience.
- Cognitive and resilient supply chains: enable real-time disruption management and faster recovery.
- Sustainable fulfillment practices: reduce environmental impact while enhancing brand trust.
Further reading:
- E-commerce Fulfillment Trends Companies Should Consider
- The Best 5 Ecommerce Fulfillment Companies For Your Business
- Omnichannel eCommerce Solutions for Business Growth
What is eCommerce fulfillment?
eCommerce fulfillment is the end-to-end process that turns an online order into a delivered (or returned) product, which is no doubt the strategic revenue and retention lever for B2B leaders transforming retail and omnichannel commerce.
This part of the supply chain includes operations like storage, inventory management, order management, packing, shipping, returns, post order tracking, etc.
Shipments, returns, inventory, warehousing, and omnichannel routing must be treated as integrated tech services (OMS, WMS, PIM, CRM + carrier APIs) to deliver predictable cost, speed, and CX at scale, making it the backbone of modern retail operations.
It can be said that even before you understood the concept of fulfillment, it has always been an integral part of your business from the beginning.
Transform your ideas into reality with our services. Get started today!
Our team will contact you within 24 hours.
Why eCommerce fulfillment matter for business leaders?
Statista shows that 60% of retailers now outsource at least part of their fulfillment, with 20% fully relying on 3PL partners, demonstrating a global shift toward tech-enabled, automated operations.
For C-level executives, this means fulfillment is no longer optional but core to:
- Strengthening digital trust, with consistent, accurate, on-time delivery.
- Unlocking scalability, especially during peak seasons or international expansion.
- Enhancing margins, by optimizing inventory, routing, and warehouse efficiency.
- Building a unified commerce ecosystem, where online and offline data flows in real time.
With rising complexity in order volumes, SKUs, and omnichannel journeys, leaders must ensure their fulfillment systems are integrated, automated, and data-driven.
Key steps in eCommerce fulfillment
Modern eCommerce fulfillment includes multiple interconnected operations that determine delivery speed, accuracy, and customer experience, which is a critical lever for operational efficiency, cost savings, and scalability.

1. Warehousing
Warehousing is the first aspect of order fulfillment that stores inventory in an organized fashion for better accessibility. Specifically, according to ShipBob, it is known as the process of storing physical goods or inventory in a warehouse or storage facility before they are sold or distributed, and most of them are very high-volume and fast paced places with product being moved constantly.
Warehouses safely and securely store items is the key factor influencing locating the products easily and quickly, and maintaining a track of your inventory in a better convenient manner. As eCommerce grows, warehouses have shifted toward tech-driven, high-velocity environments.
Core functions of modern warehousing:
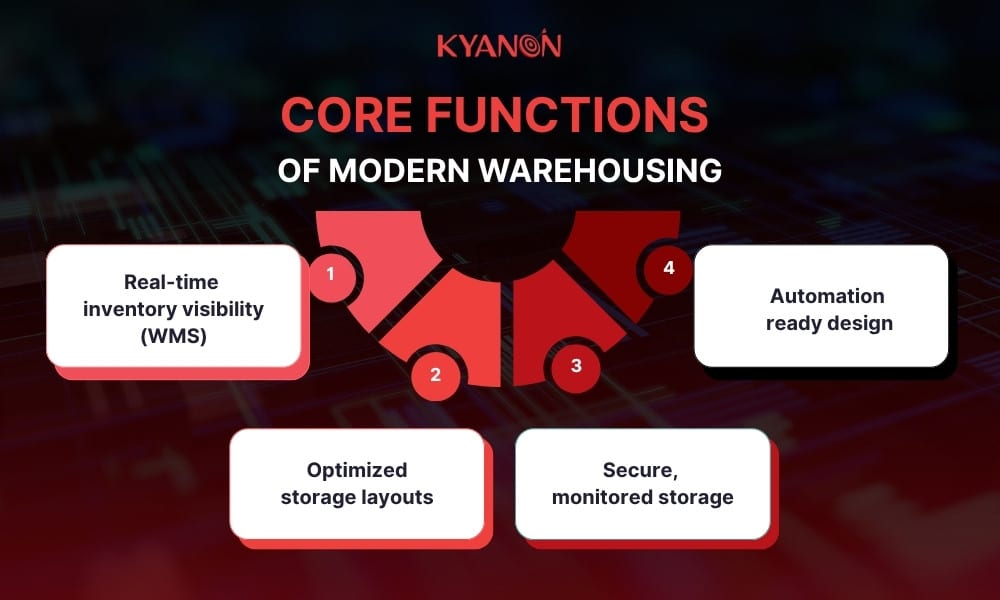
- Real-time inventory visibility (WMS): Reduces stockouts and improves demand planning.
- Optimized storage layouts: Faster pick paths and higher order accuracy.
- Secure, monitored storage: Minimizes shrinkage and misplacements.
- Automation-ready design: Supports AMRs, conveyors, and robotic picking systems.
2025 insight: Automation is accelerating
According to MHI Industry Report 2024, despite earlier market concerns, warehouse automation is now scaling faster than expected:
- Global automation adoption increased by 40% over the last two years.
- Robotics adoption is projected to increase from 41% to 83% over the next five years.
- Inventory optimization tech is expected to rise from 58% to 92%.
For instance, according to DHL’s news release, DHL has invested $1.17B in automation and uses 7,500+ robots, with 90% of warehouses deploying at least one automation or digital technology.
2. Inventory Management
The next crucial operation included in eCommerce fulfillment is inventory management, which is the monitoring of an eCommerce business’s stocked goods including storing inventory, ordering and restocking inventory, and inventory forecasting to assess customer demands and forecast in advance for your business.
Not only does correctly managing inventory imply proactively reordering the right inventory quantity for stockouts and backorders prevention, but also, it can be a source of leverage for eCommerce companies looking to increase efficiency and reduce operational costs. Rachel Andrea Go explained that with the right configuration, it will allow businesses to better manage their cash flow, predict and plan for sales velocity, and ensure a seamless buyer experience.
Key objectives & tech enablers of inventory management
|
Objective |
What it means |
Tech leaders use |
|
Stock accuracy |
Ensure real-time item availability |
WMS + RFID, IoT sensors |
|
Restock efficiency |
Automate replenishment before stockouts |
Predictive analytics + ERP |
|
Cost optimization |
Reduce dead stock & overstocks |
AI demand forecasting |
|
Cash-flow health |
Align stock with revenue cycles | Inventory forecasting tools |
For instance, retailers using AI-driven forecasting have achieved up to 30% reduction in overstocking and 20% fewer stockouts (McKinsey 2024). This directly impacts profitability and customer satisfaction.
3. Order Management
Order management is the command center for tracking and processing all orders across multiple sales channels. It connects eCommerce platforms, warehouses, payment systems, and customer service tools.
What an effective order management system (OMS) provides:

- Unified view of all orders across website, marketplaces, POS, and social commerce.
- Automatic routing to the nearest or most efficient fulfillment location.
- Instant syncing with WMS and inventory systems.
- Real-time status tracking for customers and internal teams.
C-level impact:
A connected OMS reduces manual intervention by up to 80%, cuts fulfillment time, and enables omnichannel models like BOPIS, ship-from-store, or curbside pickup.
4. Pick and Pack Fulfillment
The picking and packing process will proceed after an order is received in the eCommerce fulfillment. It refers to using a picking list to retrieve items from storage as soon as an order is placed online, and packing is the act of putting all ordered stuff in a box or poly mailer together with any necessary packing materials. Picking and packaging require complete accuracy and precision so that no inaccurate order is packed and delivered to the customer.
Why pick & pack matters:
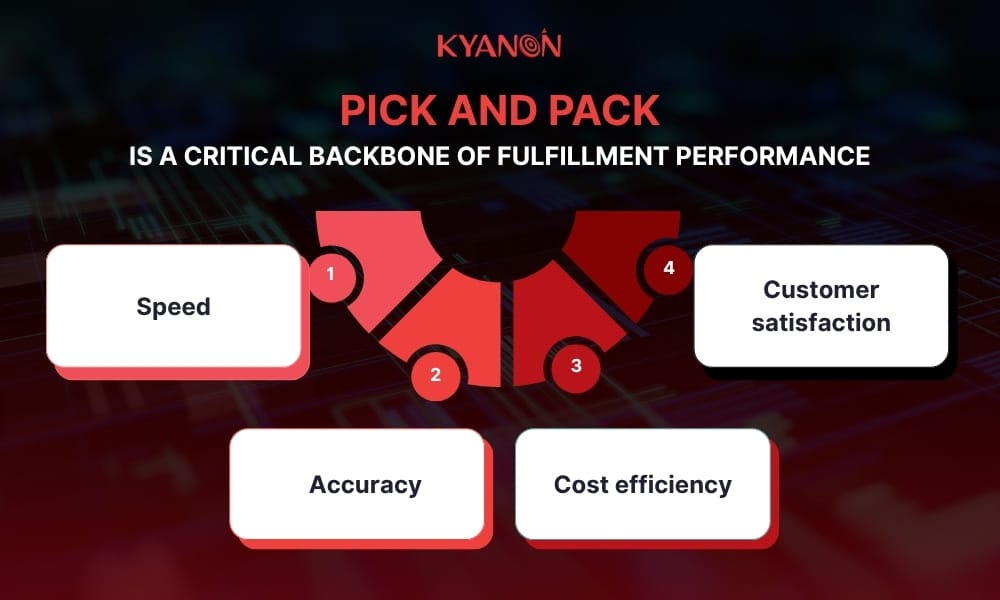
- Speed: Automated picking can improve efficiency by 2–3x.
- Accuracy: Reduces wrong-item shipments that hurt brand trust.
- Cost efficiency: Less manual handling = lower labor cost.
- Customer satisfaction: Proper packaging reduces returns due to damage.
5. Shipping
Shipping is the final-mile execution that decides whether customers return to your brand. It includes label creation, carrier selection, dispatching orders, and handling delivery tracking.
Three key shipping factors to optimize:

- Shipping costs: Dynamic rate shopping can reduce costs by 10–20%.
- Packaging options: Right-sized packaging lowers shipping fees & damage.
- Real-time tracking: Essential for customer transparency and fewer support tickets.
6. Returns Management
Returns in eCommerce fulfillment involves receiving, assessing, and processing returned items into the available stock. ShipBob showed that 92% of customers state they will buy something from an online store again if returns are easy, which demonstrates how eCommerce returns policy plays a vital role in customer experience improvement and the importance of ease of return to eCommerce shoppers as it can be a key factor influencing your sales.
Besides, by having optimized returns management, it can lead to better profit margins by reducing transportation spend, to reselling items that would have been a complete loss if disposed of upon return. Furthermore, by offering options to your customers who wish to return items that make it easier for them, it can go a long way to boost customer satisfaction. Lastly, returns management can help you identify ways to reuse, resell or recycle materials.
What modern returns management includes:
- Automated return labels.
- Integration with OMS for instant refund updates.
- Reverse logistics routing rules.
- Options like drop-off, in-store return, courier pickup.
- Recycle/refurbish/resell workflows.
- Common eCommerce fulfillment models for business
Quick comparison table of common eCommerce fulfillment models
|
Criteria |
In-House Fulfillment | 3PL Fulfillment | Dropshipping | Hybrid Fulfillment |
|
How it works |
Merchant stores, picks, packs, and ships orders internally |
A logistics provider manages warehousing, picking, packing, and shipping | Supplier stores inventory and ships directly to customers |
Combines in-house and 3PL: some products handled internally, others outsourced or shipped via 3PL |
|
Best for |
Small businesses, early-stage brands, low order volume |
Growing companies needing scalability, faster fulfillment, multi-channel operations | New sellers, low-budget startups, brands testing new markets or products |
Businesses with mixed product types, seasonal demand, or international expansion |
|
Initial investment cost |
High |
Medium | Very low |
Medium–high (depends on in-house portion and 3PL contracts) |
|
Operating cost |
High | Flexible based on usage | Nearly zero |
Flexible: mix of fixed in-house cost + variable 3PL cost |
|
Order processing time |
Fully controlled, limited by internal resources |
Fast (with the right partner) | Dependent on supplier |
Fast and adaptable: in-house for priority orders, 3PL for volume/remote areas |
|
Quality control |
Very high |
Medium–high (when SLA enforced) | Low |
High for in-house items, medium for outsourced items |
|
Scalability |
Slow and costly |
Fast, supported by existing infrastructure | Fast but hard to guarantee quality |
Fast and flexible: can scale 3PL portion while keeping control of key products |
|
Order personalization |
High |
Possible on request | Rare |
High for in-house products, limited for 3PL portion |
| Branding capability | High |
Medium (depends on partner) |
Very low |
Medium–high: in-house maintains branding, 3PL may limit options |
1. In-house fulfillment
In-house fulfillment (self-fulfillment) is the DIY approach where merchants store, pack, and ship orders themselves. It works for small brands with low order volume, but it becomes unsustainable as demand grows due to increased labor and storage requirements.
- Pros:
- No outsourcing or third-party storage fees
- Full control over packaging and product quality
- Ideal for early-stage businesses with limited orders or tight cash flow
- Cons:
- Difficult to scale as volume increases
- Time-consuming and resource-heavy
- Lacks professional logistics expertise and bulk-shipping discounts.
2. Third-party logistics (3PL)
3PL fulfillment is a model that allows you to outsource or hand over the management of your distribution infrastructure to a specialized logistics company that will handle your entire eCommerce fulfillment flow within its own fulfillment center.
- Pros:
- Faster, more efficient order processing.
- Easily scale with higher-order volume.
- Access to logistics expertise and new sales channels.
- Cons:
- Less control over packaging and the final delivery experience.
3. Dropshipping
Dropshipping lets you sell products without holding inventory. When a customer orders, the supplier ships directly to them. This reduces upfront costs and helps test new markets, but offers less control over fulfillment, inventory, and branding. Profit margins per sale are also lower.
- Pros:
- Low startup investment required.
- Easy to test new markets and products.
- No need for storage or handling inventory.
- Cons:
- Limited control over inventory and fulfillment
- Product quality and customization may suffer
- Lower profit margins per sale
- Branding opportunities are reduced
4. Hybrid fulfillment
Hybrid fulfillment combines in-house order processing with third-party logistics (3PL) or other fulfillment methods. Businesses can manage certain products internally while outsourcing others, such as international shipments, high-volume periods, or low-margin items.
- Pros:
- Flexible: handle some orders in-house, outsource others via 3PL.
- Cost-effective: lower warehouse costs, optimize shipping rates.
- Faster delivery: 3PL network brings products closer to customers.
- Brand control: maintain packaging & quality for key products.
- Scalable for seasonal peaks or international expansion.
- Cons:
- Complex management: needs robust inventory & order systems.
- Quality consistency: multiple channels may affect standards.
- Higher setup: integrating in-house + 3PL requires tech & training.
Trends of eCommerce fulfillment for business
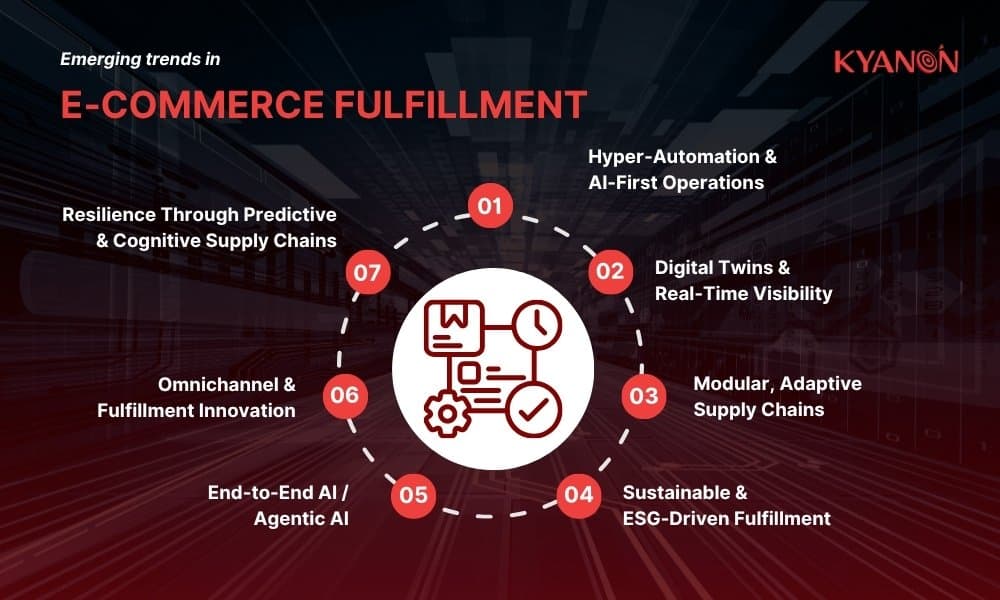
1. Hyper-automation & AI-first operations
AI, autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and smart document processing accelerate warehouse operations, reduce errors, and cut delivery times.
Example: As of 2025, Amazon operates 750,000+ robots in its warehouses. According to Business Insider, Morgan Stanley estimates that the robotics program could save the company up to US$10 billion annually by 2030.
2. Digital twins & real-time visibility
Digital twins provide virtual replicas of warehouses, inventory networks, and transportation routes. This allows proactive issue detection, predictive planning, and agile responses to demand spikes or disruptions.
Example: In a DHL + Tetra Pak warehouse in Asia, the digital twin system uses IoT sensors and real-time data to simulate workflows, predict bottlenecks, and optimize layout, improving operational efficiency and enabling proactive decision-making.
3. Modular, adaptive supply chains
Modular architectures allow businesses to quickly scale, re-route, and optimize operations. Augmentative AI supports humans in decision-making while automating repetitive tasks.
Example: Unilever leverages modular supply chain systems and hybrid fulfillment models, allowing fast rerouting and scaling during seasonal demand spikes.
4. Sustainable & ESG-driven fulfillment
Real-time data and predictive analytics optimize energy use, reduce carbon emissions, and support ESG compliance. Consumers and regulators increasingly favor sustainable fulfillment practices.
Example: IKEA uses predictive analytics and green logistics to reduce carbon emissions, optimize transportation, and comply with global ESG standards.
5. End-to-End Agentic AI
Agentic AI can autonomously handle procurement, planning, and execution, reducing operational inefficiencies and cutting supply chain costs by up to ~30%, according to Gartner, Inc.
Example: Deloitte reports that companies like Alibaba employ autonomous AI for procurement, inventory allocation, and order execution, reducing supply chain costs significantly.
6. Omnichannel & micro-fulfillment
Integrating retail stores, e-commerce sites, apps, and hyperfocal micro-warehouses allows faster delivery, better stock utilization, and a unified customer experience.
Example: Walmart is scaling its automated micro-fulfillment capabilities, converting parts of its store network into mini-warehouses for fast delivery. Its “Accelerated Pickup & Delivery” (APD) model supports same-day reach for ~93% of U.S. households; Walmart also aims for 55% of its order volume to be automated by FY26.
7. Cognitive & Resilient Networks
Cognitive supply chains combine IoT, AI, and predictive analytics to sense, decide, and react to disruptions instantly. Recovery speed is now a key differentiator.
Example: DHL uses its Resilience360 platform, powered by AI and IoT, to monitor global risks in real time, predict disruptions (weather, geopolitical, demand), and proactively reroute or mitigate supply chain issues.
Why choose Kyanon Digital as your partner for eCommerce fulfillment?
Kyanon Digital helps retailers and eCommerce brands across Southeast Asia optimize fulfillment operations by combining advanced technology expertise with a customer-first approach.
Here’s how Kyanon Digital makes a difference:
- Tailored fulfillment solutions: We design and implement in-house, 3PL, dropshipping, or hybrid fulfillment models that align with your business size, product types, and market strategy.
- Seamless omnichannel integration: From e-commerce platforms, mobile apps, to physical stores, we ensure a unified and efficient fulfillment workflow for faster delivery and better customer experience.
- Data-driven insights: Leveraging AI, WMS, OMS, and predictive analytics, we help businesses optimize inventory, route orders efficiently, and forecast demand accurately.
- Proven expertise: With experience supporting top Southeast Asian retailers and brands, we combine technical know-how with practical strategies to reduce fulfillment costs, improve delivery accuracy, and scale operations sustainably.
Case study: Kyanon Digital transforms eCommerce fulfillment with AI-driven BI & data warehouse

Challenge:
The client struggled with fragmented fulfillment data, manual reporting, and delayed insights, making it difficult to monitor inventory, track orders, and optimize multi-location operations in real time.
Solution:
Kyanon Digital implemented a centralized Data Warehouse with AI-powered reporting and Power BI dashboards, streamlining fulfillment workflows across warehouses and stores:
- Centralized order and inventory reporting: Unified data from all locations for accurate stock visibility and faster decision-making.
- Automated approval and tracking: Reduced manual errors and accelerated order monitoring.
- Real-time BI dashboards: Enabled executives to track fulfillment KPIs, delivery performance, and inventory levels instantly.
Results & impact:
- Reduced reporting and monitoring errors by 80%.
- Improved inventory accuracy and fulfillment speed.
- Enabled data-driven decisions across nationwide operations.
- Provided scalable, future-ready infrastructure for eCommerce growth.
Read more: AI-Driven BI & Data Warehouse For A Leading Retail Corporation.
Conclusion
eCommerce fulfillment plays a vital role in your eCommerce business, and it is important to do it properly if you want to achieve a good delivery experience for your customers.
Kyanon Digital hopes this article will provide useful information and help you have a correct view of eCommerce fulfillment to make rational decisions related to this aspect.
Partnering with Kyanon Digital ensures your eCommerce fulfillment operations are efficient, scalable, and optimized to deliver exceptional customer experiences. Contact Kyanon Digital today!

















