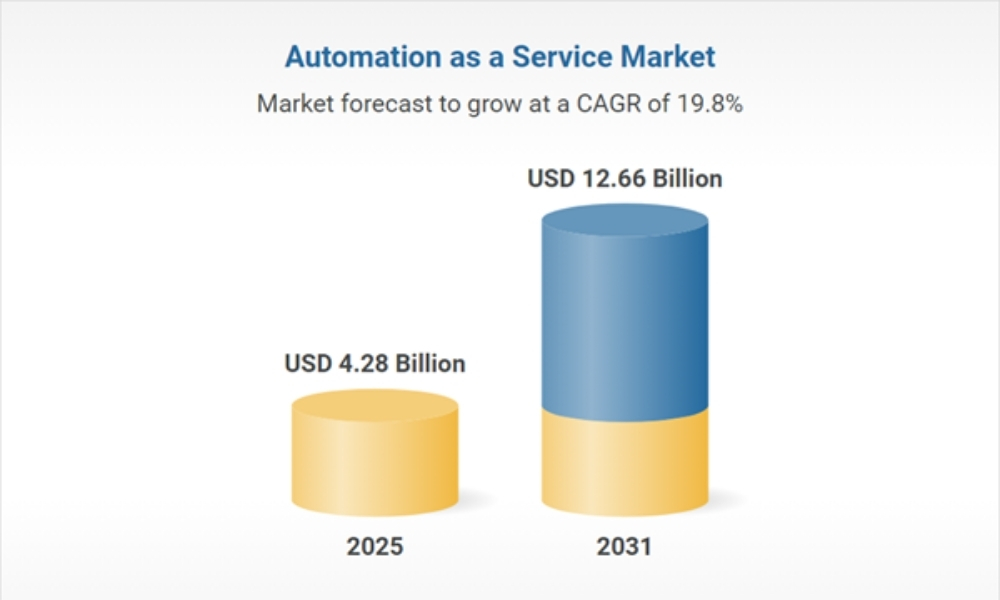
The landscape of business process automation in 2026 has shifted from simple task execution to complex autonomous orchestration. Research & Markets indicates that the global automation sector reached approximately $4.28 billion in 2025 and is projected to achieve $12.66 billion by 2031, and 95% of decision-makers affirmed that process automation helped their organizations meet operational efficiency targets (2024 State of Process Orchestration).
Despite this high success rate in efficiency, many organizations still struggle with fragmented automation and legacy technical debt that prevent scalable transformation.
To bridge this gap between isolated efficiency and true scalability, in this guide, Kyanon Digital explores the critical trends in business process automation in 2026, including agentic AI, hyperautomation, and strategic governance.
Despite this growth, many organizations struggle with “automation silos” and legacy technical debt that prevent scalable transformation. To remain competitive, leaders must transition from manual workflow oversight to designing integrated, autonomous ecosystems where AI agents and humans collaborate seamlessly.
Key takeaways
- Business process automation in 2026 becomes a core operating strategy, shifting from isolated task automation to autonomous, AI-driven enterprise execution.
- Agentic AI and multi-agent systems are redefining ai business process automation by enabling reasoning, planning, and end-to-end workflow orchestration.
- Hyperautomation is now the baseline, integrating AI, ML, RPA, and process mining into unified orchestration platforms across the enterprise.
- Low-code and citizen development accelerate deployment but require strong governance to avoid fragmented systems and technical debt.
- Embedded governance and compliance are mandatory as global regulations and AI risk management become central to automation design.
- Sustainable automation and ESG integration link efficiency, cost reduction, and energy optimization with long-term enterprise resilience.
- Competitive advantage will depend on orchestration, not tool adoption, enterprises that align AI, humans, data, and governance will scale automation successfully.
Further reading:
- Top 10 Tech Trends 2026 by Gartner
- Top 16 AI Automation Companies in Singapore
- How Can Startups Harness AI Agents As A Service?
From task automation to autonomous enterprise ecosystems
Traditional Robotic Process Automation (RPA) focused on rule-based, repetitive tasks such as data entry and system transfers. While effective for efficiency gains, it lacks the intelligence and orchestration required for complex, cross-functional operations and real-time decision environments (IBM).
Market signals confirm this transition. Workato’s Work Automation Index 2024 reports a 400% year-over-year increase in automated business processes using generative AI, highlighting rapid enterprise movement toward hyperautomation and AI-driven automation platforms.
This shift is driven by growing structural pressure on enterprises:
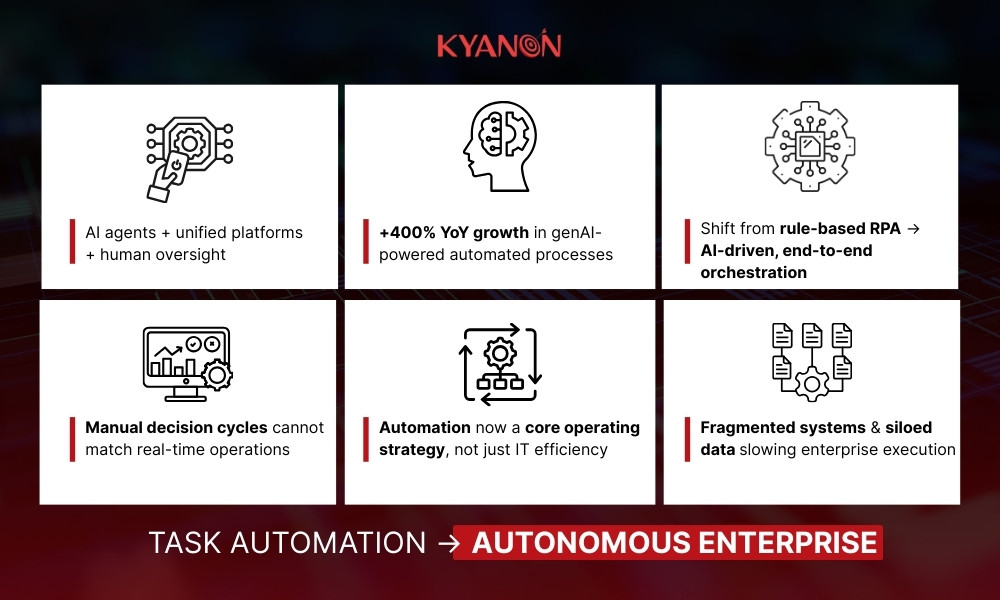
- Fragmented systems and siloed data continue to slow execution despite heavy digital investment
- Manual decision cycles cannot keep pace with real-time operational demands
- Automation pilots often fail to scale across functions due to governance and integration gaps
- AI adoption without process redesign creates additional complexity instead of efficiency
As a result, automation is moving beyond an IT efficiency initiative to become a core enterprise operating strategy. Leading organizations are building autonomous ecosystems where AI agents orchestrate processes, employees supervise exceptions, and unified platforms connect data, workflows, and decisions in real time.
Transform your ideas into reality with our services. Get started today!
Our team will contact you within 24 hours.
The 6 macro trends redefining automation in 2026
Quick overview table
|
Trend |
What’s changing |
Why it matters for business |
|
Agentic AI & multi-agent systems |
Shift from rule-based RPA to reasoning AI agents coordinating across systems |
Enables end-to-end execution, faster decisions, and scalable autonomous operations |
|
Hyperautomation baseline |
AI, ML, RPA, and process mining unified into one orchestration layer |
Cuts cost, replaces fragmented tools, and scales automation enterprise-wide |
|
Low-code & citizen development |
Business teams build automation directly; governance becomes essential |
Accelerates deployment while requiring strong architecture and oversight |
|
Digital twin of organization |
Real-time simulation and control towers for process optimization |
Reduces rollout risk and enables predictive, data-driven automation |
|
Embedded governance & compliance |
Regulations and AI governance built into automation design |
Ensures secure scaling and faster expansion into regulated markets |
|
Sustainable automation & ESG |
Automation linked to energy efficiency and ESG KPIs |
Lowers cost and carbon footprint while strengthening resilience |
Agentic AI & multi-agent systems
Agentic AI is emerging as a core driver of business process automation in 2026, shifting enterprises from static workflows toward autonomous systems that can reason, coordinate, and execute across functions.
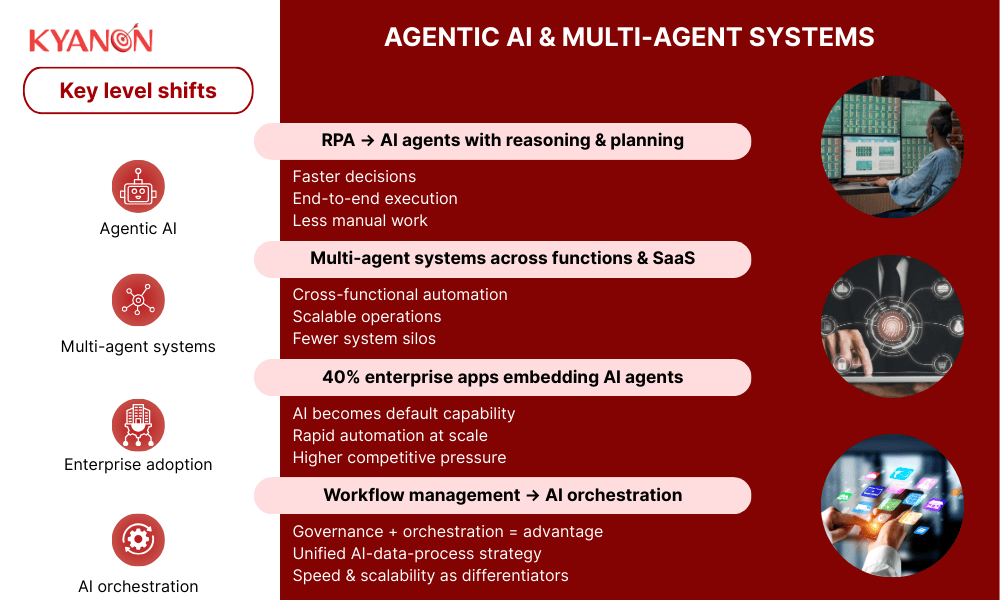
- Automation is evolving from rule-based RPA and scripts to AI agents capable of reasoning, planning, and autonomous task execution.
- Multi-agent systems can coordinate across SaaS platforms and enterprise functions to complete complex, multi-step processes with minimal human intervention.
- Gartner forecasts 40% of enterprise applications will embed AI agents by 2026, accelerating enterprise adoption of agentic automation.
- Leadership focus is moving from managing workflows to orchestrating AI agents, data, and human oversight across unified automation platforms.
Impact on business
- Agentic automation enables end-to-end execution across SaaS ecosystems, reducing reliance on fragmented tools and manual coordination.
- AI-driven agents are expected to automate significant portions of enterprise service and support operations, with Cisco revealing that 68% of customer interactions will be handled by AI by 2028, highlighting rapid enterprise-scale deployment.
- Competitive advantage will depend on orchestration capabilities: enterprises that integrate AI agents, governance, and platforms effectively will gain speed, scalability, and operational resilience as automation becomes a core operating model.
Hyperautomation becomes the baseline
Hyperautomation is becoming the default model for business process automation in 2026, as enterprises move from fragmented tools to unified, end-to-end orchestration across operations.
Key shifts
- Disconnected tools are being replaced by unified platforms combining AI, ML, RPA, and process mining
- Automation is moving from isolated tasks to end-to-end orchestration across entire value chains
- Process mining enables real-time visibility to identify, optimize, and scale automation opportunities
- Unified orchestration layers are becoming essential to manage workflows, data, and automation across systems
Impact on business
- Hyperautomation allows enterprises to scale automation while maintaining governance and operational visibility
- Organizations implementing hyperautomation can reduce operational costs by up to 30% while improving efficiency and accuracy (Kissflow)
- Competitive advantage will depend on the ability to orchestrate automation across platforms and functions at enterprise scale
Low-code/no-code & citizen developers
Low-code and no-code platforms are accelerating business process automation in 2026, enabling business teams to build and deploy automation without relying fully on IT.
Key shifts
- Non-technical teams across HR, Finance, and Sales increasingly build their own workflows and apps using low-code platforms.
- By 2026, 75% of new applications will be developed using low-code technologies, showing rapid enterprise adoption of citizen development (Hostinger).
- Up to 80% of low-code users will come from outside IT, reducing reliance on central development teams and accelerating automation deployment (Hostinger).
- Governance and security frameworks are becoming mandatory as decentralized automation expands across departments.
Impact on business
- Low-code enables faster automation rollout and reduces IT backlog, allowing enterprises to scale process automation across functions.
- However, without strong governance, citizen-built automation can create technical debt, integration risks, and fragmented systems.
- Competitive advantage will depend on balancing the speed of citizen development with centralized orchestration, security, and enterprise architecture.
Digital twin of the organization (DTO)
Digital twins of the organization are emerging as a critical layer of business process automation in 2026, enabling enterprises to simulate, monitor, and optimize operations before deploying automation at scale.
Key shifts
- Leading enterprises are using DTOs to simulate process changes instead of relying on assumptions.
- Real-time control towers integrate live operational data to visualize workflows, bottlenecks, and dependencies.
- Organizations can run “what-if” scenarios to test automation impact across global operations before rollout.
- DTOs are becoming a foundation for predictive, data-driven decision-making and continuous optimization.
Impact on business
- DTOs significantly reduce operational risk by preventing disruption during large-scale automation deployment.
- Enterprises gain real-time visibility across systems, improving resilience and decision accuracy.
- Simulation-driven automation helps avoid “automated chaos” caused by fragmented or poorly tested rollouts.
- Competitive advantage will depend on the ability to model, test, and orchestrate automation changes across complex global operations.
Embedded governance & compliance
Embedded governance is becoming essential to business process automation in 2026, as global regulations require compliance to be built into automation design from the start.
Key shifts
- Regulations such as the EU AI Act and data sovereignty laws make compliance a core design requirement.
- Governance, auditability, and risk controls must be embedded directly into AI and automation workflows.
- By 2026, 60% of Fortune 100 companies are expected to appoint a Head of AI Governance to manage rising regulatory complexity, with leaders such as Sony, Bank of America, and UBS already establishing dedicated oversight roles (Data Storage Asia).
- Compliance is shifting from post-deployment fixes to built-in architecture and policy controls.
Impact on business
- Built-in compliance reduces legal and operational risks during automation scaling.
- Enables faster global deployment across regulated markets.
- Organizations with embedded governance can scale automation more securely and sustainably.
Sustainable automation & ESG
Sustainable automation is becoming a core pillar of business process automation in 2026, as enterprises align automation strategy with ESG goals, energy efficiency, and waste reduction across operations.
Key shifts
- Automation is increasingly designed to reduce energy consumption, resource waste, and carbon footprint across digital and physical operations.
- Process automation is being used to optimize supply chains, logistics, and resource planning for sustainability outcomes.
- ESG metrics are shifting from reporting indicators to operational KPIs embedded directly into automation workflows.
- Enterprises are integrating sustainability data into automation platforms to track emissions, efficiency, and compliance in real time.
Impact on business
- Automation reduces cost + energy waste: AI-enabled smart operations can cut energy consumption by up to 30%, linking automation directly to ESG and operational efficiency (McKinsey).
- ESG becomes an operational KPI: Embedding sustainability into automation improves regulatory readiness and investor confidence as ESG reporting shifts from disclosure to execution.
- Energy-efficient automation = competitive edge: Rising AI and data center energy demand (IEA) makes sustainable automation and carbon-aware operations critical for scalable, resilient enterprise growth.
Automation impact by industry – What changes in practice
Retail & eCommerce – unified commerce
Business process automation enables real-time personalization and frictionless commerce across digital and physical channels.
- Hyper-personalization in checkout and offers (agentic AI + customer data orchestration).
- Frictionless checkout & biometric auth reduce abandonment.
- Dark-store/Q-commerce (<30 min) driven by automated fulfillment and routing.
- Automated returns workflows cut RTO cost and speed refunds (process mining + RPA).
Impact: Faster conversion, lower fulfillment cost, and better CX through end-to-end orchestration.
FMCG & CPG – margin survival game
BPA shifts value from volume to precision, such as SKU-level, neighborhood-aware distribution and promotions.
- Predictive distribution to SKU & micro-regions (ML + DTO simulations).
- Smart field force with next-best-action automation (low-code rules + AI agents).
- Traceability & compliance automated across supply chain (policy-as-code).
Impact: Margin protection via lower stockouts, optimized promotions, and fewer compliance penalties.
Manufacturing, F&B & industrial – Factory as a nervous system
Automation turns plants into real-time nervous systems, combining sensors, AI vision, and orchestration.
- Predictive maintenance improves OEE and uptime.
- Cobots + AI vision for QC cut defects substantially and increase throughput.
- Automation enforces safety protocols and throughput SLAs.
Impact: Higher OEE, lower defect rates, safer operations, and automation become core production infrastructure.
BFSI – From AI assistants to autonomous partners
Financial services move from assistive bots to agentic systems that execute compliance and liquidity decisions in real time.
- Agentic compliance: real-time KYC/AML and fraud prevention (audit trails required).
- Hyper-automated wealth management (portfolio rebalancing, tax harvesting).
- Invisible payments and liquidity optimization via AI orchestration.
Impact: Faster compliance response, lower operational risk, and improved client outcomes with policy-embedded automation.
Logistics & supply chain – Connected intelligence
End-to-end orchestration links warehouse robotics, routing, and customs to create resilient supply chains.
- Warehouse orchestration for robot fleets and dynamic slotting.
- Predictive routing that adapts to weather and port congestion (DTO + ML).
- Automated customs workflows shorten clearance time and paperwork.
Impact: Lower lead times, improved resilience to disruptions, and reduced logistics cost per order.
Education & travel
BPA personalizes learning and travel experiences end-to-end using AI agents and unified platforms.
- Adaptive learning paths that auto-tune content to learner progress (AI + low-code).
- AI travel assistants personalize entire journeys and automate bookings/changes.
Impact: Higher engagement, reduced service friction, and scalable personalization.
Core technology stack leaders must understand
Enterprise business process automation in 2026 is defined by how well organizations architect their core automation stack, where the right technologies enable scalable, AI-driven, and resilient operations across global business functions.
Quick overview table
|
Technology |
Role in 2026 |
Business impact |
|
Agentic AI |
Core engine of ai business process automation, enabling systems to reason, decide, and execute across workflows |
Drives semi-autonomous operations, faster decision cycles, and scalable execution across functions |
|
Process mining |
Evidence-based discovery layer for business process automation, revealing bottlenecks and automation opportunities |
Reduces process errors and rework, improves accuracy and ROI of automation initiatives |
|
Low-code platforms |
Rapid development layer enabling cross-functional teams to deploy BPA business process automation at scale |
Speeds deployment up to 10× and reduces IT backlog while expanding automation across departments |
| Cloud-native BPA |
Scalable orchestration foundation connecting AI, data, and workflows across regions and systems |
Enables resilient global operations, real-time integration, and continuous automation scaling |
Insight for business: The wrong automation stack creates fragmented systems and “automation chaos”; the right stack enables scalable, secure, enterprise-wide execution.
Executive strategic priority matrix 2026
Business process automation in 2026 is shifting from isolated efficiency initiatives to a core executive agenda shaping capital allocation, talent models, risk governance, and customer experience strategy across the enterprise.

Capital allocation → Digital labor infrastructure
- Investment shifts from expanding human labor to building scalable digital labor using AI agents and automation platforms.
- Automation becomes a long-term operating infrastructure, not a short-term cost optimization.
- Priority: fund unified automation platforms, data orchestration, and AI-driven operations.
Talent strategy → AI orchestration skills
- Up to 40% of the workforce will need reskilling toward AI orchestration, automation design, and process governance roles (IBM).
- Demand rises for hybrid talent combining business process, data, and automation expertise.
- Priority: build internal capabilities to manage AI-driven business process automation at scale.
Risk management → Embedded AI governance
- Automation introduces model drift, bias, compliance, and data sovereignty risks across operations.
- Governance must be embedded into automation design, not added post-deployment.
- Priority: establish AI governance frameworks, auditability, and policy-based automation controls.
Customer experience → Predictive service models
- Shift from reactive self-service to predictive, automated service orchestration.
- AI-driven automation enables real-time personalization, proactive support, and seamless journeys.
- Priority: integrate automation with customer data platforms to deliver predictive and autonomous service experiences.
The “hidden” factors most automation projects fail to address
Quick overview table
|
Factor |
Risk |
Business action |
|
AI FinOps & token costs |
Uncontrolled AI usage drives cost spikes |
Implement AI FinOps + usage governance |
|
DTO & simulation gap |
No testing → rollout failures |
Use DTO to simulate before scaling |
|
Culture resistance |
Teams block automation adoption |
Position AI as augmentation, not replacement |
|
Legacy systems |
Old tech limits integration |
Modernize to API-first architecture |
|
IP risk |
Unclear ownership of AI outputs |
Add HITL review + governance |
| Tech fragmentation |
Regulations + vendor lock-in |
Adopt multi-cloud, multi-model strategy |
Business process automation initiatives in 2026 fail less from technology gaps and more from overlooked economic, organizational, and governance realities. Leaders must manage these hidden variables to scale automation sustainably.
Token economy & AI FinOps
AI-driven business process automation introduces variable operating costs that can scale unpredictably without governance.
- AI shifts cost structure from fixed software licenses to usage-based token and inference costs
- Uncontrolled model inference and API calls can create sudden budget overruns within hours
- CFO and CTO alignment on AI FinOps, usage monitoring, and cost-per-process metrics becomes mandatory
- FinOps dashboards and usage throttling increasingly embedded into automation platforms
Business implication: Enterprises treating AI as infrastructure now implement AI FinOps and inference budgeting to prevent runaway operating costs and ensure predictable automation ROI.
Digital twin of the organization
Automation deployment without simulation creates high operational risk across complex enterprise systems.
- DTOs simulate workflows, dependencies, and automation impact before rollout
- Real-time control towers detect bottlenecks and process conflicts early
- Enables “what-if” testing across regions, supply chains, and business units
Business implication: DTO-driven automation significantly reduces failed deployments and prevents “automated chaos” during large-scale transformation initiatives.
Culture: augmentation over replacement
Organizational resistance remains one of the top reasons automation programs stall.
- Middle management resistance often blocks automation scaling
- Leading firms incentivize employees to automate their own workflows
- New roles emerge: process architects, AI workflow owners, automation strategists
Business implication: Companies that position automation as augmentation, not replacement, achieve faster adoption and stronger internal innovation pipelines.
Legacy system debt
Legacy infrastructure is one of the biggest constraints on enterprise automation scaling.
- AI agents layered on 15–20-year-old ERP systems create integration fragility
- Lack of API-first architecture limits orchestration and data flow
- Core system modernization becomes a prerequisite for advanced automation
Business implication: Enterprises prioritizing API-first modernization and composable architecture scale automation faster and avoid integration-driven failures.
IP contamination risk
AI-generated outputs introduce legal and intellectual property uncertainty.
- Not all AI-generated content or code has clear copyright ownership
- Enterprises implement human-in-the-loop (HITL) review for critical outputs
- Creative and product teams are required to add original contribution layers
Business implication: Clear governance over AI-generated assets protects enterprise IP and reduces legal exposure in product, marketing, and software development.
Geopolitical tech fragmentation
Automation strategy must adapt to rising regulatory and infrastructure fragmentation globally.
- Sovereign AI policies require localized data and model deployment
- Multi-model and multi-region architecture reduces geopolitical risk
- Vendor lock-in to a single AI provider increases long-term exposure
Business implication: Enterprises adopt multi-model, multi-cloud automation strategies to maintain operational resilience across regions and regulatory environments.
2026 executive red-flag checklist
2026 executive red-flag checklist

- Shadow AI inside the enterprise
- Are teams using unapproved AI tools or agents without governance, data control, or security oversight?
- Model drift after deployment
- Are AI models monitored and retrained regularly, or do they lose accuracy and business relevance within 3–6 months?
- Vendor lock-in risk
- Can core AI/automation workloads migrate across platforms or providers within 48 hours if needed?
- AI cost visibility
- Do leaders have real-time tracking of token usage, inference costs, and cost-per-process ROI?
- Built-in compliance
- Are governance, auditability, and data sovereignty embedded into automation design from day one?
- Scalability beyond pilot
- Can automation scale across functions and regions, or still stuck in isolated proof-of-concept stages?
Why choose Kyanon Digital as your partner?
Unified integration & automation expertise
Kyanon Digital enables end-to-end business process automation by integrating systems, data, and workflows into a single scalable execution layer.
Composable, scalable architecture
Enterprises gain future-ready automation with composable, cloud-native, and API-first architecture designed for flexibility and growth.
Built-in governance, security, and performance
Automation solutions are delivered with embedded security, monitoring, and compliance to ensure scalable and risk-controlled operations.
Proven enterprise delivery capability
With strong engineering, data, and consulting expertise, Kyanon delivers enterprise-grade automation aligned with measurable business outcomes.
Flexible engagement for transformation at scale
From strategy to implementation, Kyanon supports enterprises with adaptable delivery models to accelerate automation and digital transformation.
Case study: How Kyanon Digital enabled AI-driven automation for a leading retail enterprise

Challenge
The retailer struggled with fragmented data, manual reporting, and slow decision cycles across departments. Disconnected systems limited real-time visibility and prevented scalable business process automation.
Solution
Kyanon Digital implemented an AI-driven BI and data warehouse platform that centralized data, automated reporting workflows, and enabled real-time dashboards for cross-functional decision-making. Automated approval and data pipelines replaced manual processes and siloed reporting.
Impact
- Real-time operational visibility across business units
- Faster, data-driven decision cycles with reduced manual reporting
- Scalable automation foundation for analytics, forecasting, and process optimization
- Improved data accuracy, governance, and cross-department alignment
Business value
The project demonstrates how unified data, AI, and automation can move enterprises from fragmented reporting toward integrated, decision-centric business process automation at scale.
Read more: AI-Driven BI & Data Warehouse For A Leading Retail Corporation
Conclusion – Automation is now a CEO problem
Business process automation in 2026 is no longer an IT initiative but a core enterprise operating strategy. Automation decisions now shape cost structures, execution speed, governance, and competitive positioning at the executive level.
The winners will not be the organizations that automate the most tasks, but those that orchestrate best across AI, human teams, data, and governance. As automation evolves into autonomous enterprise ecosystems, leadership focus must shift from tool adoption to orchestration design, risk control, and scalable execution.
In this new landscape, automation becomes a boardroom priority: a strategic capability that determines how fast enterprises can adapt, scale, and compete in an AI-driven economy.
Ready to scale automation beyond pilots?
Contact Kyanon Digital to assess your automation maturity, build unified orchestration, and turn automation into a true enterprise growth engine.