In today’s digital landscape, building trust and safeguarding your business are paramount. One crucial line of defense is Understanding Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations. KYC is a set of procedures businesses use to verify customer identities and assess potential risks.
This blog dives deep into the world of KYC for businesses. We’ll break down the key components, explain its importance, and guide you through the KYC process. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how KYC keeps your business secure and compliant.
1. What is KYC?
According to Swift, KYC, or “Know Your Customer”, is a set of processes that allow banks and other financial institutions to confirm the identity of the organizations and individuals they do business with, and ensures those entities are acting legally.
Effective KYC protects companies from doing business with organizations or individuals involved in illegal activity, such as money laundering, terrorist financing or corruption. It also allows financial institutions to get a better understanding of their customers’ businesses, which can provide valuable insights for financial institutions.

2. Why is KYC Important for Businesses?
In an effort to combat illegal activities that exploit the financial industry for money laundering or illicit transactions, governments and central banks worldwide have expanded their Know Your Client (KYC) policies. These regulations now cover nearly every aspect of the global financial ecosystem.
The increased focus on KYC is driven by the rising prevalence of financial crimes globally. Additionally, the growing interconnections between financial institutions and corporate entities across borders have made it more challenging to prevent illegal financial activities. Regulators have responded by enhancing and reinforcing KYC checks to keep up with these developments.

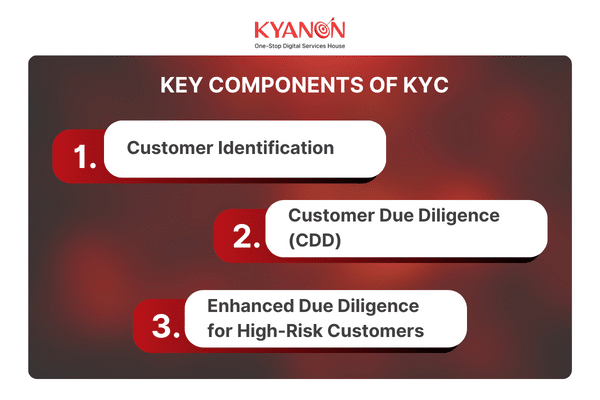
3. Key Components of KYC
3.1. Customer Identification
- Personal Identification Documents
Personal identification documents encompass government-issued forms of identification, such as passports, driver’s licenses, and national identity cards. These documents serve to verify an individual’s identity, including details like their name, date of birth, nationality, and photograph.
- Corporate Identification Documents
Corporate identification documents encompass articles of incorporation, business registration certificates, and tax identification numbers. These documents serve to establish the legal existence and ownership structure of a corporate customer.
3.2. Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
- Purpose and Nature of the Business Relationship
Financial institutions must comprehend the purpose and nature of their business relationships with customers. This involves identifying the types of products and services the customer seeks, the anticipated transaction volume, and the reasons for initiating the relationship.
- Source of Funds
Financial institutions must verify the source of funds used by customers for transactions. This verification ensures that the funds are legitimate and not derived from illicit activities, such as money laundering or terrorist financing.
3.3. Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) for High-Risk Customers
- Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs)
Politically exposed persons (PEPs) are individuals who hold prominent public positions, domestically or internationally, and may have a higher risk of corruption.
Financial institutions must perform enhanced due diligence (EDD) for PEPs, which includes obtaining senior management approval and closely scrutinizing their transactions.
- Customers from High-Risk Jurisdictions
Financial institutions must apply enhanced due diligence (EDD) measures to customers from high-risk jurisdictions, as identified by the FATF or national regulators.
These customers may present a higher risk of money laundering or terrorist financing due to weak regulatory environments or high levels of criminal activity in their home countries.
- Customers with Unusual Transaction Patterns
Customers displaying unusual transaction patterns or activities that deviate from their risk profile may require enhanced due diligence (EDD). This involves investigating the reasons for such transactions and, if necessary, filing suspicious activity reports (SARs) with the relevant authorities.
4. The KYC Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Customer Identification – Collect basic customer information such as name, date of birth, address, and contact details, and obtain identification documents like government-issued IDs and utility bills for verification.
Step 2: Customer Due Diligence (CDD) – Assess the customer’s risk level based on their profile, verify the authenticity of provided documents, and cross-check information against external databases and watchlists.
Step 3: Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) – Identify high-risk customers, such as PEPs or those from high-risk jurisdictions, and conduct additional checks, including senior management approval and detailed background investigations.
Step 4: Continuous Monitoring – Implement systems to monitor transactions for suspicious activities and periodically review and update customer information and risk assessments.
Step 5: Record Keeping and Reporting – Maintain comprehensive records of customer information and due diligence measures, and report any suspicious activities to relevant authorities, complying with all regulatory requirements.
Step 6: Training and Awareness – Regularly train staff on KYC procedures and regulatory requirements, keep KYC policies updated with regulatory changes, and continuously improve the KYC process based on feedback and audits.

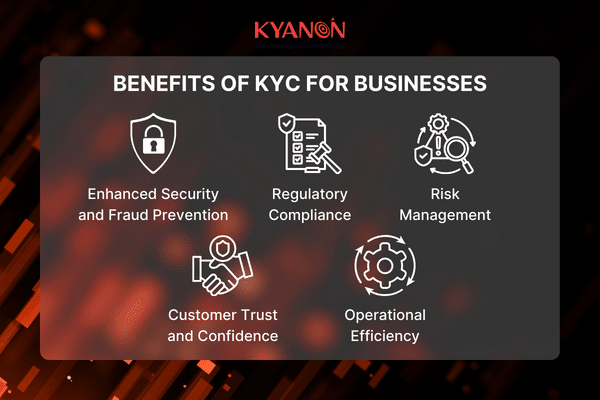
5. Benefits of KYC for Businesses
5.1. Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention
Verifying customer identities reduces the risk of fraud and identity theft, ensuring only legitimate customers access services.
5.2. Regulatory Compliance
Complying with AML and CTF regulations helps businesses avoid legal penalties and reputational damage.
5.3. Risk Management
Assessing customer risk profiles enables businesses to mitigate potential losses and protect against financial threats.
5.4. Customer Trust and Confidence
Demonstrating a commitment to security and compliance builds trust and loyalty among customers.
5.5. Operational Efficiency
Automating KYC processes streamlines customer onboarding, reduces manual workload, and cuts operational costs.
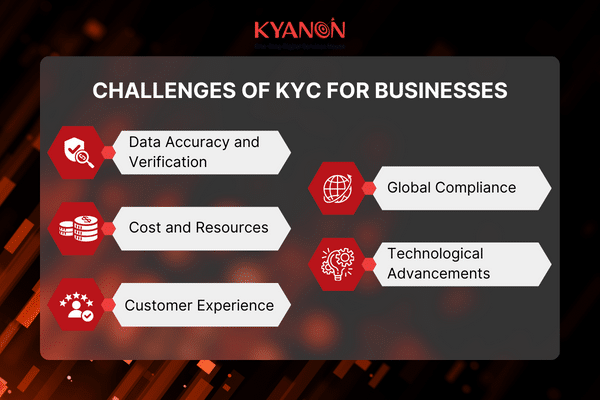
6. Challenges of KYC for Businesses
Know Your Customer (KYC) processes are essential for businesses, but they come with their own set of challenges. Here are some common ones.
6.1. Data Accuracy and Verification
Ensuring the accuracy of customer information can be difficult. Businesses must verify identities, addresses, and other details to prevent fraud.
6.2. Cost and Resources
Implementing robust KYC procedures requires investment in technology, personnel, and training. Smaller businesses may struggle with these costs.
6.3. Customer Experience
Striking a balance between thorough verification and a seamless customer experience is challenging. Lengthy processes can frustrate customers.
6.4. Global Compliance
Businesses operating internationally must navigate varying regulations and compliance requirements across different jurisdictions.
6.5. Technological Advancements
Keeping up with evolving technology (such as biometrics and AI) for identity verification is crucial but can be complex.
7. Who needs KYC?
Financial Institutions: Banks, investment firms, and insurance companies require KYC to comply with regulations and manage financial risks.
Fintech Companies: Online payment processors and cryptocurrency exchanges use KYC to prevent fraud and money laundering.
E-commerce Platforms: Online retailers implement KYC to verify the identity of sellers and buyers, ensuring secure transactions.
Telecommunications Companies: Mobile network operators use KYC to authenticate customers and prevent identity theft.
Gaming and Gambling Operators: Casinos and online betting platforms require KYC to comply with regulations and prevent underage gambling and money laundering.
8. Conclusion
At Kyanon Digital, we excel in leveraging innovative solutions to enhance operational efficiency and security for our clients. Our expertise extends to implementing KYC and eKYC processes, allowing businesses to verify customer identities swiftly and securely. With our comprehensive approach, we empower businesses to streamline operations, comply with regulations, and build trust with their customers.
Contact us for more information about KYC initiatives for your business.