In software, “composable” means building with interchangeable pieces, like LEGO bricks. Composable commerce takes this concept to e-commerce, letting you pick best-in-class tools from different vendors instead of being stuck with an all-in-one solution.
According to Gartner, a leading research and advisory company, composable commerce will emerge as an increasingly important approach in the enterprise software space, with ecommerce at the forefront.
Read on and discover the future of building your online store with Kyanon Digital!
1. What is Composable Commerce?
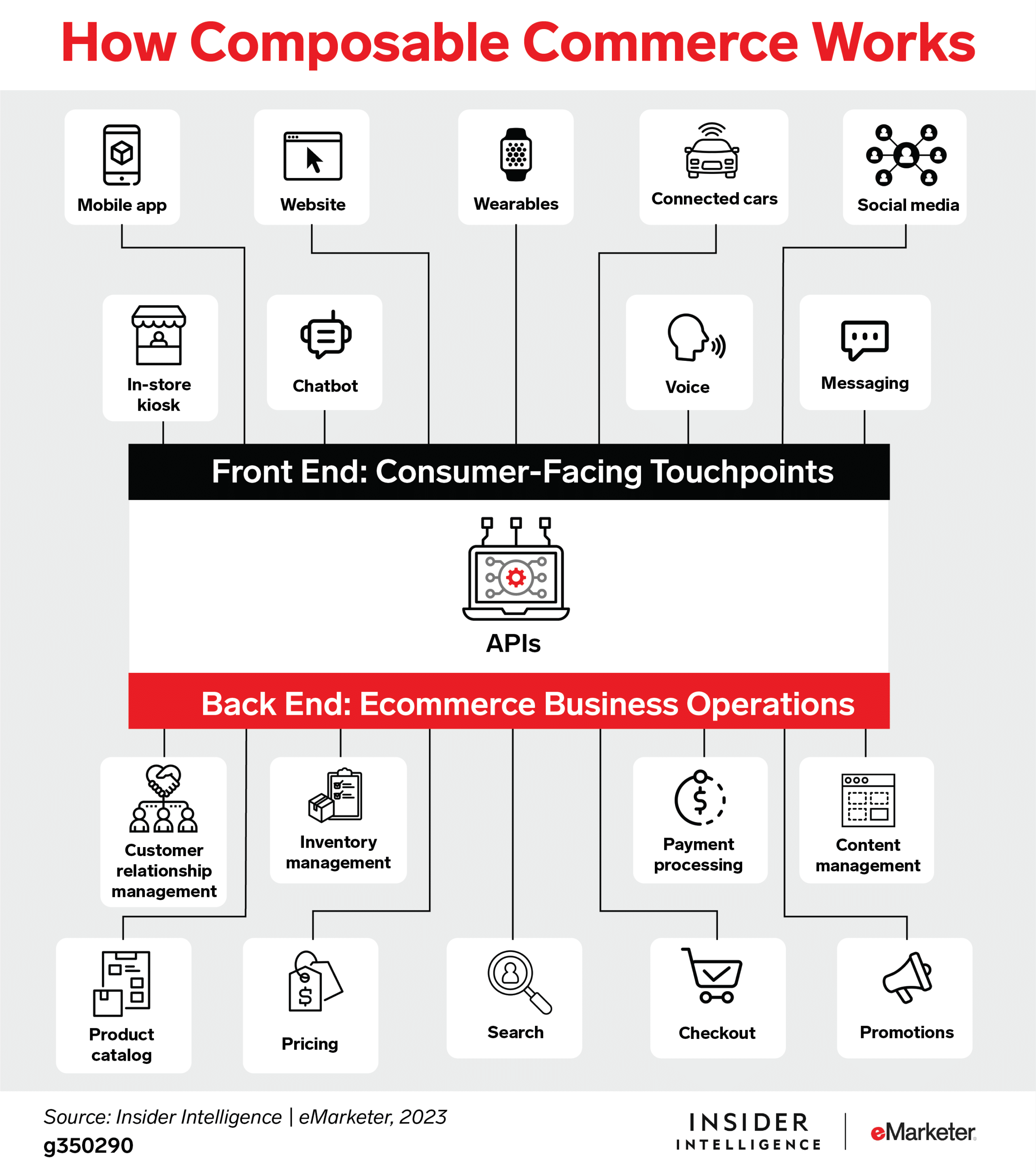
Composable commerce is a modular approach to building ecommerce platforms, where businesses can select and integrate various technologies to create a tailored solution. This flexibility allows for quick adaptation to market changes and customer needs, promoting innovation and offering a competitive advantage.
Composable commerce is able to deploy this by using packaged business capabilities (PBCs). PBCs are the building blocks of the larger solution, all of which are connected via application programming interfaces (APIs). The core capabilities of an ecommerce platform may still be used, but will act more like a “peer” among other solutions than a “core” around which other solutions fit.
2. Composable Commerce vs. Headless Commerce
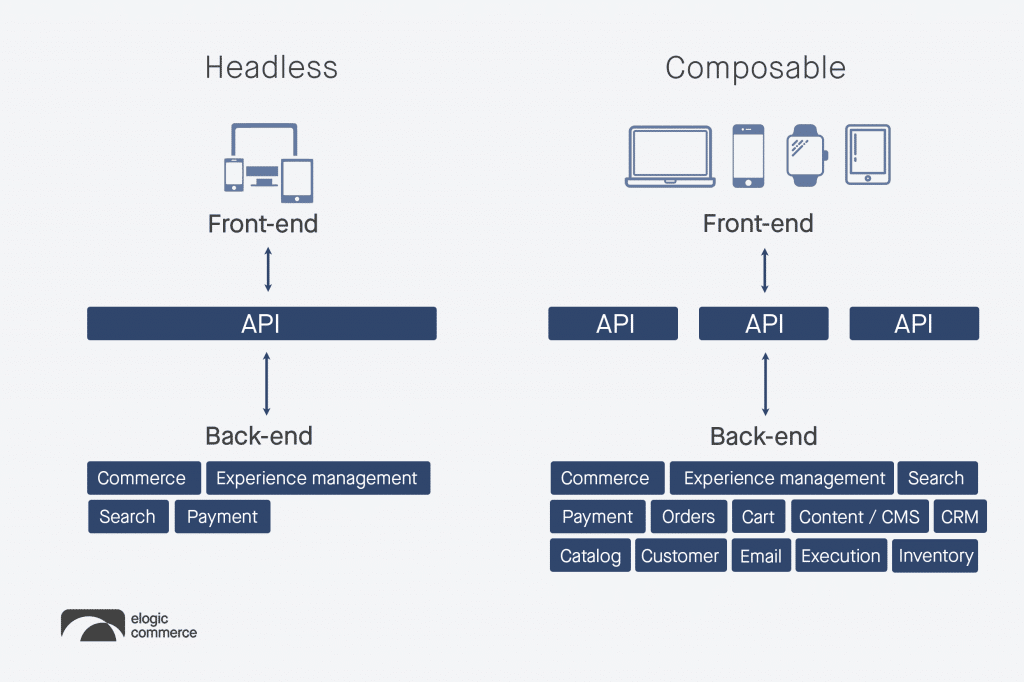
Headless commerce laid the groundwork by separating the front-end presentation layer from the back-end functionality. Composable commerce represents a continued evolution, enabling businesses to dissect their commerce platform into distinct services.
While a headless system usually involves front-end components depending on a unified back end, a composable system ensures independence for each business capability. Embracing composable solutions often begins with a decoupled front end as a solid initial step in the enterprise’s journey.
3. What are packaged business capabilities?
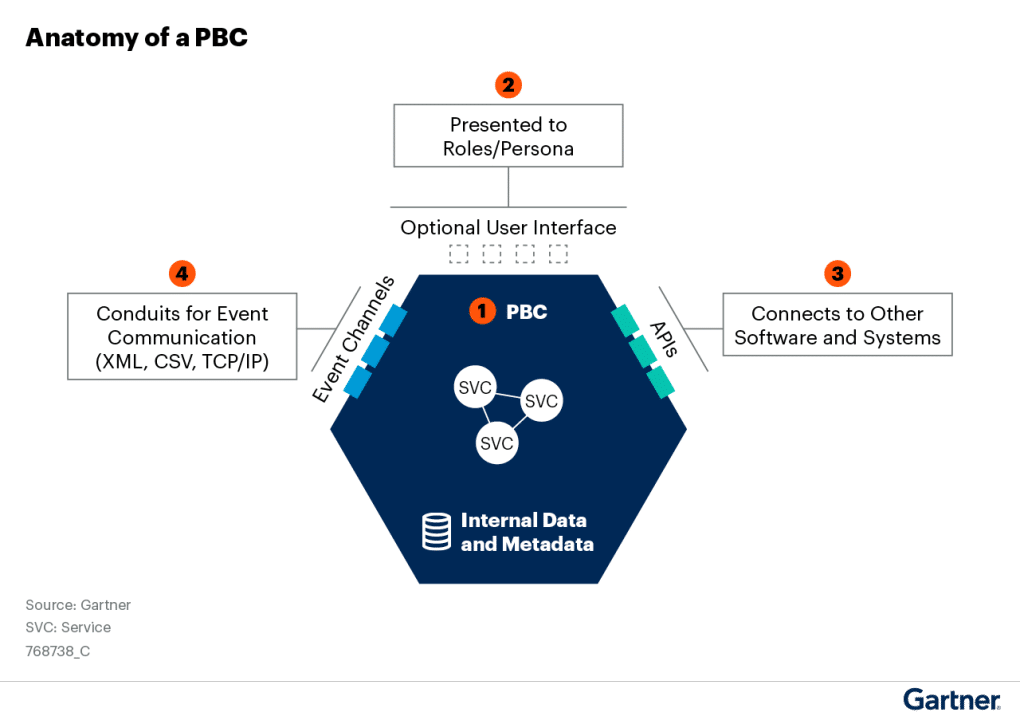
Packaged business capabilities (PBCs) are software components designed to represent specific business functions. Essentially, a PBC is dedicated to a particular business capability and is crafted to be functionally complete, ensuring autonomy. A composable commerce solution comprises these PBCs, seamlessly interconnected through a unifying API, regardless of whether they originate from the same or different vendors.
PBCs are created to align to a business outcome. Examples of PBCs include:
- Storefront
- Catalog
- Promotions
- Cart
- Checkout
- Payment
- Search
4. What is the evolution of composable commerce?
In the realm of ecommerce technology, commerce suites were once considered the epitome. Referred to as monolithic commerce suites, they encompassed a multitude of commerce-related functions within a unified software system. Notable vendors in this category included Oracle, IBM, and SAP.
These suites, characterized by their extensive scope, intricately integrated with various facets of digital commerce, such as:
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
- Customer relationship management (CRM)
- Warehouse management (WMS)
- Product lifecycle management (PLM)
- Content management system (CMS)
The primary objective was to consolidate all functionalities into a singular suite. However, this approach led to the development of monolithic structures that exhibited deep interdependence and lacked modularity.
5. Benefits of Composable Commerce
Composable commerce presents a multitude of advantages for businesses seeking to enhance their ecommerce systems. Here are several ways it can contribute to greater flexibility, increased profits, and an enhanced user experience:
5.1. Flexibility and Agility for Businesses
Composable commerce empowers businesses to tailor their ecommerce systems by selecting components that align most effectively with their needs and requirements. By adopting a modular software component approach, organizations can carefully choose and configure elements that best suit their strategies and objectives. While this setup may require more time for initial implementation, it significantly enhances future business agility by avoiding reliance on a rigid monolithic solution.
5.2. Increased Efficiency and Profitability
Embracing a best-of-breed, modular approach allows businesses to cherry-pick components that align precisely with their ecommerce needs. This reduces the time and resources spent on unnecessary or inefficient elements, ultimately saving both time and money in the long run. The focus can then be directed towards essential aspects such as serving customers and driving revenue.
5.3. Improved User Experience
Composable commerce enables businesses to select best-in-class components, including content management systems and marketing automation software. This, in turn, facilitates targeted and personalized touchpoints, such as customized product recommendations and personalized content. The result is an improved overall user experience that caters to individual preferences and needs.
6. Challenges of Composable Commerce
Composable commerce introduces a higher level of complexity compared to traditional all-in-one platforms. To determine whether a composable commerce approach aligns with your needs and objectives, consider the following factors:
6.1. Complexity
Achieving seamless integration among various PBCs (Packaged Business Capabilities) and services is pivotal, as these components collaborate to provide a unified customer experience. However, this process can be intricate and time-intensive, especially if your team lacks technical expertise. Managing diverse components with distinct contracts, APIs, data structures, and dependencies poses challenges. Unless your company is digitally mature with an experienced engineering team and intricate delivery requirements, composable commerce may not be the most suitable choice.
6.2. Maintenance
In a composable commerce architecture, individual components of the solution incur separate costs, leading to potential accumulation of maintenance and update expenses. Depending on the number of PBCs sourced from various vendors, these costs can escalate.
6.3. Slower Speed-to-Market
Opting for composable commerce may not be ideal if speed-to-market is a top priority. As it operates in a pro-code environment, the process may be slower compared to platforms that enable you to swiftly compose different aspects of your architecture using pre-built commerce components while ensuring a quick launch.
In conclusion, when navigating the intricate landscape of commerce architecture, it is imperative to weigh the complexities, maintenance considerations, and speed-to-market priorities. As you assess these factors, it becomes evident that Kyanon Digital stands out as an industry expert with unparalleled expertise in Composable Commerce. With a track record spanning over a decade, Kyanon Digital has consistently demonstrated its prowess in navigating the evolving digital commerce terrain.
Contact us to receive a free consultation about Composable Cọmmerce.


